Ćwiczenie jako czynnik wyzwalający migrenę vs. profilaktyka: Znalezienie równowagi
Ćwiczenia a Migreny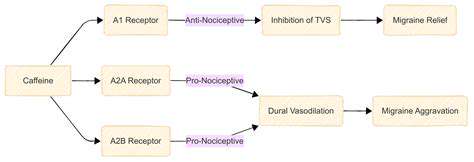
Read more about Ćwiczenie jako czynnik wyzwalający migrenę vs. profilaktyka: Znalezienie równowagi
Ustalanie granic w celu ochrony zdrowia i zapobiegania migrenom
Znalezienie dostępnych hobby, które nie wywołują migreny
Tłumaczenie badań nad migreną na praktyczne strategie dnia codziennego
Związek między napięciem mięśni szyi a częstotliwością migren
Rozpoznawanie migreny hemiplegicznej: objawy i genetyka
Wpływ izolacji społecznej na postrzeganie bólu przewlekłego
Cykliczny zespół wymiotny i jego związek z migreną
Rola ciśnienia płynu mózgowo-rdzeniowego w niektórych typach bólu głowy
Rola neuropeptydów (poza CGRP) w migrenie
Stres oksydacyjny jako czynnik w patofizjologii migreny
Związek między PCOS (zespołem policystycznych jajników) a migreną
Krytyczna ocena informacji zdrowotnych online dotyczących migreny

