Introduction to Identifying Root Causes
Understanding the Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used to identify the underlying reasons for problems or challenges within an organization. By focusing on the root causes, it becomes easier to develop effective solutions that address the problem at its source rather than merely treating its symptoms.
Many organizations suffer from recurring issues that can be traced back to unresolved root causes. The failure to identify these can lead to wasted resources, loss of productivity, and declining employee morale. Therefore, conducting an RCA is crucial for long-term success and sustainability.
Moreover, RCA can drive continuous improvement and foster a culture of accountability within teams. By understanding what leads to certain challenges, teams can work collaboratively to implement changes that prevent future occurrences, thus enhancing overall performance.
Common Challenges Faced in Identifying Root Causes
Identifying root causes can often be complicated by various factors, including inadequate data collection, biases in analysis, and a lack of structured methodologies. Many practitioners may jump to conclusions without thoroughly investigating the problem, leading to ineffective solutions.
Additionally, organizational silos can impede open communication and collaboration, making it difficult to gather diverse perspectives that may shed light on the true nature of a problem. This lack of teamwork can hinder the RCA process and result in incomplete solutions.
Another significant challenge is the time and resources required to perform a comprehensive root cause analysis. Organizations may feel pressured to quickly address issues, which often leads to superficial fixes rather than a thorough investigation of the root cause. Prioritizing RCA is essential but can be easier said than done amid operational demands.
Methods and Techniques for Effective Root Cause Analysis
There are several popular methods for conducting root cause analysis, each with its unique advantages. Techniques such as the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa), and Pareto Analysis are commonly utilized to facilitate structured thinking and help teams systematically uncover the roots of their challenges.
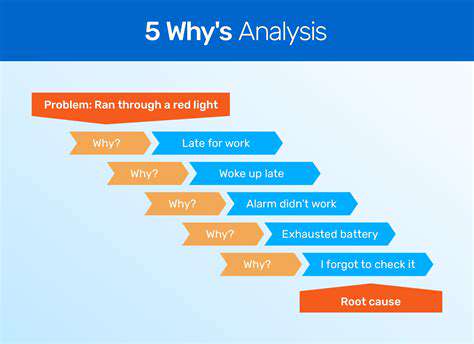
The 5 Whys technique involves asking "why" repeatedly, aiming to drill down to the underlying cause of a problem. This method is simple yet effective, particularly for organizations with limited resources looking for quick insights.
Meanwhile, the Fishbone Diagram helps in visualizing relationships between a problem and its potential causes. By categorizing causes into different branches, teams can organize their thoughts and pinpoint the primary contributors to an issue, making this approach particularly valuable during brainstorming sessions.
Implementing Solutions Based on Root Cause Insights
Once root causes have been identified, the next step is formulating appropriate solutions. This can include procedural changes, training programs, or even revising company policies to prevent future occurrences of the identified challenges. The key is to ensure that the solutions not only address the symptoms but also mitigate the root causes effectively.
It's equally important to involve stakeholders when implementing solutions. Engaging those affected by the changes fosters buy-in and ensures that proposed solutions are viable in practical settings.
Finally, establishing a feedback loop is essential for ongoing improvement. By monitoring the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and being open to revisiting the root cause analysis process, organizations can adapt and refine their approaches as needed, thus fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
The Significance of Root Cause Analysis
The Importance of Identifying Root Causes
Root cause analysis (RCA) is essential for effectively addressing challenges within any organization. By pinpointing the source of problems, teams can develop targeted strategies to prevent recurrence. This proactive approach saves time and resources in the long run. Instead of merely treating symptoms, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Failure to identify root causes often leads to a cycle of repeated issues. Teams may find themselves implementing temporary fixes without truly understanding the underlying problems. This can result in frustration, wasted effort, and diminished morale among employees. A clear focus on root causes can break this cycle and enable lasting solutions.
Moreover, RCA facilitates better decision-making. When leadership understands the factors contributing to each challenge, they can allocate resources effectively and prioritize initiatives that yield the best outcomes. This strategic alignment ensures that all team members are working towards the same goals, enhancing overall productivity.
Embracing root cause analysis also supports a culture of accountability. As employees learn to investigate challenges more deeply, they become more responsible for their work. This empowerment fosters collaboration and innovation, ultimately leading to higher-quality results.
Methods and Tools for Root Cause Analysis
There are various methodologies for conducting root cause analysis, each with its strengths and applications. One popular method is the "5 Whys," which involves asking "why" multiple times until the fundamental cause is identified. This technique promotes a deeper understanding of the issue at hand.
Another effective tool is the fishbone diagram, also known as the Ishikawa diagram. This visual representation helps teams categorize potential causes into relevant groups, enabling more structured brainstorming sessions. By organizing thoughts this way, teams can easily identify relationships between various factors contributing to the problem.
Data analysis also plays a crucial role in root cause analysis. Organizations can leverage statistical methods to identify patterns and correlations in their data. By analyzing historical data, teams can uncover hidden trends that may point to systemic issues requiring attention.
Finally, it’s crucial to involve cross-functional teams in the RCA process. Diverse perspectives provide the opportunity to uncover insights that might be missed by a single department. Engaging team members from different backgrounds fosters collaboration and creates a shared commitment to addressing challenges.
Methods for Identifying Root Causes
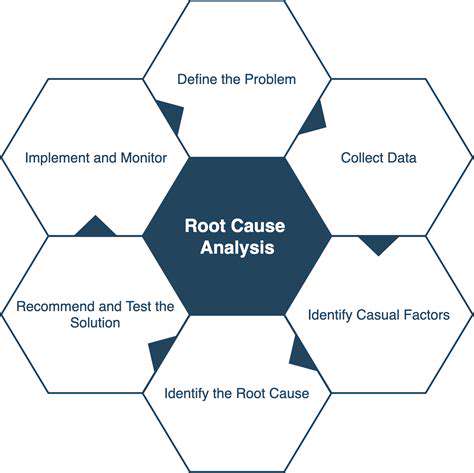
1. Defining the Problem Clearly
One of the most critical steps in identifying root causes is to define the problem clearly. A vague understanding of the issue can lead to misdiagnosis and ineffective solutions.
Start by gathering as much information as possible about the problem. This could include data, testimonials from affected individuals, and insights from stakeholders involved.
Use tools like the Five Whys technique, which involves asking "why?" repeatedly until you reach the foundational cause. This helps to dig deeper into the issue rather than stopping at surface-level symptoms.
Creating a clear problem statement can also be beneficial. This statement should outline who is affected, what the problem is, when it occurs, and any specific conditions associated with it.
Ensuring everyone agrees on the problem's definition lays a strong foundation for effective root cause analysis and promotes collaboration among team members.
2. Utilizing Root Cause Analysis Tools
Employing specific root cause analysis (RCA) tools can greatly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of identifying challenges. Some popular tools include Fishbone Diagrams and Pareto Analysis.
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as an Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagram, allows teams to visually map out various potential causes of a problem, categorizing them into different categories such as people, processes, methods, and materials.
Pareto Analysis involves identifying the most common causes of an issue and focusing on those that will have the highest impact when addressed, based on the Pareto Principle that states 80% of effects come from 20% of causes.
Using flowcharts can also help in visualizing the sequence of events leading to the problem, providing insight into where the root cause may lie.
Using multiple tools in conjunction can provide a comprehensive overview of the situation, helping teams to leave no stone unturned in their analysis.
3. Gathering Input from Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders in the root cause analysis process is crucial. Their insights and perspectives can shed light on factors that may not be immediately obvious to outside observers.
Conducting interviews or surveys with those directly impacted by the problem can reveal vital information. This could include employees, customers, or partners, depending on the context of the challenge.
Facilitate brainstorming sessions where stakeholders can freely express their ideas and experiences related to the problem. This collaborative approach can generate a wealth of information.
Consider using a Delphi method, which gathers opinions from a panel of experts through multiple rounds, ensuring that all voices are heard and consensus is built.
Involving a diverse group of stakeholders not only enriches the analysis but also helps in creating buy-in for the resulting solutions.
4. Observing the Process in Action
Active observation is a powerful method for identifying root causes. By watching the processes or systems at play, one can often spot inefficiencies or anomalies that contribute to challenges.
Conducting time-and-motion studies can help pinpoint areas where delays or errors occur, revealing underlying issues that may go unnoticed in theoretical analysis.
Shadowing employees as they perform their tasks can provide firsthand insights into workflow challenges and systemic issues that might contribute to the problem.
Using tools like process mapping helps visualize workflows and identify bottlenecks or redundancies that could indicate deeper issues.
Documenting observations and comparing them with reported issues can help confirm suspicions and guide the analysis toward effective solutions.
5. Implementing and Monitoring Solutions
Once root causes are identified, it's time to implement solutions. However, the process does not end here; monitoring the effectiveness of these solutions is equally important.
Establish clear performance indicators to measure the impact of implemented solutions. This will help ascertain whether the changes are working and whether further adjustments are needed.
Regular follow-up meetings with stakeholders can keep everyone informed about progress and help address any emerging issues promptly.
It's also crucial to remain open to feedback. Continuous improvement is a vital part of the process, and adapting solutions based on real-world feedback can lead to greater success.
By combining effective implementation with ongoing evaluation, teams can not only mitigate current challenges but also build a framework for addressing future issues proactively.
Implementing Solutions Based on Identified Causes
Understanding the Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a critical process used to identify the underlying reasons for problems or challenges in various contexts, such as business operations or personal issues. By focusing on the root causes, organizations can implement solutions that are both effective and sustainable. Ignoring the root causes often leads to temporary fixes that do not resolve the underlying issues. This can result in recurring problems that ultimately consume more time and resources.
Moreover, RCA encourages a culture of continuous improvement. When teams consistently analyze and understand the reasons behind challenges, they are more likely to adopt proactive measures that enhance performance and reduce the likelihood of future issues. By creating an environment where critical thinking is valued, organizations foster innovation and adaptability.
Furthermore, implementing RCA promotes better decision-making. Leaders equipped with insights from thorough analyses can make informed choices that align with long-term goals. This strategic approach not only saves costs but also strengthens the overall operational framework. As a result, businesses can navigate challenges more effectively and maintain a competitive edge.
In summary, understanding the importance of root cause analysis is vital for any organization looking to enhance its performance and sustainability. By addressing issues at their core, teams can turn challenges into opportunities for growth and improvement.
Common Challenges Faced by Organizations
Organizations face various challenges that can impede progress and success. These challenges may range from operational inefficiencies to employee disengagement, all of which can significantly impact productivity. Identifying these issues requires a detailed assessment of current practices and employee feedback.
Another prevalent challenge is the ever-evolving market landscape. Companies must adapt to technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and competitive pressures. Failing to do so can result in obsolescence and loss of market share. To remain relevant, organizations need to be agile and responsive to changes in their environment.
Finally, communication barriers can also manifest as significant challenges. Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings, decreased collaboration, and ultimately unsatisfactory results. Organizations must prioritize clear and open communication channels to ensure that all employees are aligned with the company's goals and strategies.
By recognizing these common challenges, organizations can take the first step towards implementing effective solutions that address the unique issues they face.
Identifying Root Causes Through Data Analysis
Data analysis plays a pivotal role in identifying the root causes of challenges within organizations. By gathering relevant data, such as performance metrics and feedback, decision-makers can develop a comprehensive understanding of the issues at hand. It is essential to analyze this data from multiple perspectives to uncover patterns and correlations.
One effective method for data analysis is the use of statistical tools. These tools can help organizations identify trends over time, enabling them to make data-driven decisions. Another approach is conducting surveys and interviews, allowing organizations to gain insights directly from employees and customers.
Implementing qualitative analysis is also beneficial—it uncovers the nuances and underlying feelings associated with specific challenges. Teams that engage in group discussions or brainstorming sessions can often gain deeper insights than relying solely on quantitative data.
In summary, leveraging data analysis effectively allows organizations to pinpoint root causes. By employing a combination of statistical methods and qualitative assessments, teams can move toward crafting tailored solutions that directly address the identified challenges.
Strategic Planning for Implementing Solutions
Once root causes have been identified, organizations must develop a strategic plan to implement effective solutions. This involves outlining clear objectives and determining the necessary resources. Strategic planning ensures that solutions are not only feasible but also aligned with the organization's overall goals. As part of this process, identifying key stakeholders and involving them in the planning phases can lead to more robust and accepted outcomes.
Additionally, it is vital to establish measurable criteria for evaluating the success of the implemented solutions. Organizations can utilize key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress and make adjustments as necessary. This level of accountability fosters a culture of responsibility and encourages teams to stay committed to achieving the desired outcomes.
Moreover, considering potential risks and challenges that may arise during implementation is crucial. By proactively addressing these potential obstacles, organizations can minimize disruptions and ensure a smoother transition to new practices or policies.
Ultimately, strategic planning serves as a roadmap for successful solution implementation. When organizations invest the time and resources to meticulously plan, they are far more likely to achieve lasting improvements.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Solutions
After implementing solutions, it is essential to evaluate their effectiveness. This evaluation process allows organizations to determine if the solutions have successfully addressed the identified root causes. One effective method for this evaluation is to revisit the KPIs established during the strategic planning phase to measure actual outcomes against the expected results.
In addition to quantitative metrics, qualitative feedback from employees and stakeholders provides valuable insights into the perceived impact of the changes. Conducting follow-up surveys or focus groups can reveal how individuals feel about the effectiveness of new processes and whether they are experiencing a positive change.
Another aspect of evaluation is the need for continuous monitoring. Organizations should maintain an ongoing assessment of their solutions to ensure that they remain relevant and effective. This adaptability allows companies to make real-time adjustments and improvements as necessary.
In conclusion, evaluating the effectiveness of solutions is an ongoing process that requires attention to both quantitative and qualitative metrics. By committing to a culture of evaluation and feedback, organizations can ensure they remain on track toward achieving their objectives.