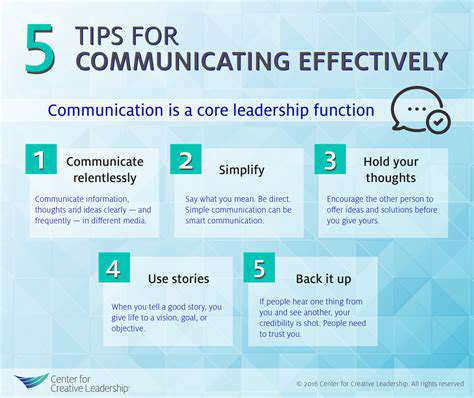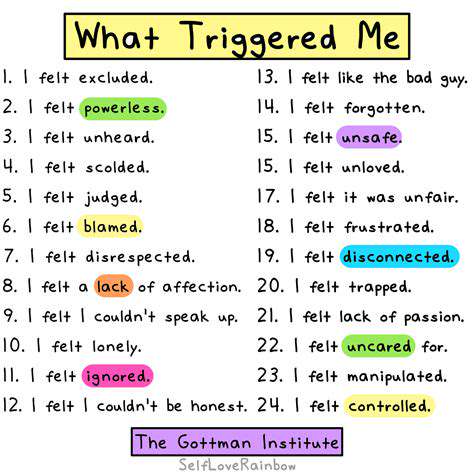
Understanding the Concept of Triggers
Triggers represent those moments that consistently spark specific emotional or behavioral reactions within us. Pinpointing these catalysts serves as the foundation for managing our responses and cultivating healthier coping strategies. The ability to recognize patterns in how we react emotionally provides invaluable insight into our psychological makeup. Grasping what sets us off emotionally matters because it equips us to foresee challenges and craft tailored approaches to handle them.
These reaction points frequently stem from past experiences or learned behaviors. While sometimes subtle enough to miss, their influence on our wellbeing can be profound. Through careful observation of our reactions and their preceding events, we gain clarity about our emotional terrain and tools to navigate it.
Common Types of Triggers
Triggers appear in various guises. External versions might involve particular individuals, environments, or sounds, while internal ones could include specific thoughts or memories. For instance, a family member's communication style or disputes with friends often serve as external triggers. Internally, negative self-perceptions, traumatic recollections, or future anxieties commonly activate responses.
The internal variety frequently originates from unresolved emotional wounds or past difficulties. Addressing these psychological triggers proves essential for maintaining emotional equilibrium. Recognizing how external and internal triggers interact helps develop comprehensive response management strategies.
Strategies for Pinpointing Triggers
Discovering your triggers demands introspection and careful monitoring. Maintaining a detailed journal where you document thoughts, feelings, and preceding events before strong emotional reactions can reveal hidden patterns and connections.
Consistent documentation builds awareness of recurring patterns and helps identify specific triggers with greater accuracy. Consider journaling techniques that capture situational details, physical sensations, thought processes, and emotional responses. This meticulous record-keeping becomes an indispensable tool for self-discovery.
The Value of Professional Guidance
While self-reflection offers benefits, professional support can significantly enhance trigger identification. Therapists provide safe environments to explore past experiences and uncover patterns influencing emotional responses. The therapeutic setting offers structure for deep emotional exploration.
Professional assistance proves particularly valuable for those struggling to identify triggers independently. Counselors offer specialized tools to understand response origins and develop effective coping mechanisms, potentially leading to substantial improvements in emotional health and overall wellbeing.
Saying No with Grace and Confidence: Protecting Your Energy

Mastering the Art of Declining
The ability to decline requests represents a vital life skill, safeguarding your time, energy, and wellbeing. This practice isn't about rudeness but rather about establishing healthy limits and honoring your needs. It requires shifting from feeling obligated to everything to recognizing personal limitations and the necessity of self-preservation.
Confidently saying no enables focus on endeavors that truly align with your values and aspirations. This prevents spreading yourself too thin, ultimately fostering greater fulfillment and productivity.
Recognizing Your Resistance Points
Identifying situations that prompt your need to decline is crucial for skill development. Are you agreeing from fear of disappointing others, people-pleasing tendencies, or fear of missing opportunities? Understanding these motivations allows proactive management and more effective responses.
Crafting Considerate Refusals
Polite declines needn't be elaborate. Simple, direct statements delivered calmly suffice, such as, I appreciate your consideration, but I can't commit to this currently. Such responses demonstrate respect while maintaining your boundaries.
Developing Assertive Communication
Assertive expression forms the cornerstone of effective refusal. It involves clearly stating needs and opinions respectfully, without aggression or passivity. This approach nurtures healthy relationships while helping others understand your limits without feeling dismissed. Practice conveying boundaries firmly yet considerately.
Cultivating Self-Respect Through Boundaries
Declining requests constitutes an act of self-respect. It acknowledges your worth, recognizing time and energy as precious resources deserving protection. Boundary-setting honors your needs and priorities, which proves fundamental for personal wellbeing and happiness. This practice empowers choices that genuinely serve you.
Moving Beyond Fear and Guilt
Overcoming reluctance to say no and associated guilt requires practice and self-compassion. Recognize that refusal doesn't reflect poorly on your character but represents necessary resource management. Self-reflection helps identify hesitation sources and develop strategies to address them. Mastering this skill is a journey permitting occasional missteps.
Protecting Your Time and Space: Creating a Sanctuary for You
Establishing Your Limits
Clear boundaries form the bedrock of time and space protection. This practice isn't selfish but acknowledges your limitations and requirements. It involves recognizing energy-draining activities, overwhelming tasks, and commitments aligning with your priorities. Defining these parameters helps prevent burnout and ensures mental/emotional capacity to thrive.
Evaluate various life domains—work, relationships, personal obligations—and honestly assess time/energy allocation. Are you agreeing to non-beneficial commitments? Understanding your boundaries creates frameworks for conscious, wellbeing-protecting choices.
Prioritizing Self-Nurturing
Self-care constitutes necessity, not luxury, for boundary maintenance. It encompasses diverse activities supporting physical, mental, and emotional health. Regular exercise, nutritious eating, sufficient sleep, and mindfulness practices form essential components. These habits not only enhance physical health but also buffer against stress and aid energy management.
Incorporating enjoyable activities—reading, music, nature time, hobbies—helps recharge. Prioritizing self-care represents an investment in overall wellbeing and boundary preservation capacity.
Designing Physical and Digital Environments
Creating dedicated physical and digital spaces conducive to focus and relaxation proves vital for boundary maintenance. Distraction-free workspaces enhance productivity and facilitate work-life transitions. This involves minimizing interruptions and employing scheduling tools.
Establishing digital boundaries matters equally. Disabling notifications, limiting social media, and scheduling email checks prevent digital distractions and maintain priority focus. This fosters healthier technology relationships and reclaims time/energy.
Communicating Your Parameters
Effectively conveying boundaries is crucial for their maintenance. This requires clearly expressing limits to family, colleagues, and friends. Honest, respectful communication prevents misunderstandings and ensures needs receive acknowledgement. Though requiring practice, this skill proves essential for healthy relationships and personal space protection.
Balancing Consistency and Adaptability
Boundary consistency ensures effectiveness, though flexibility sometimes becomes necessary. Life presents unexpected situations requiring adjustments. The key lies in remaining mindful of needs while adapting boundaries to support overall wellbeing.
Distinguishing between necessary flexibility and boundary violations proves crucial for healthy relationships and personal wellness. It involves finding personalized balance while staying true to core values.
Managing Expectations and Setting Realistic Goals: Avoiding Overwhelm
The Significance of Achievable Objectives
Realistic goal-setting prevents overwhelm and facilitates success. Overly ambitious targets often lead to consistent shortfalls, breeding frustration and defeat that undermine motivation. Understanding your capabilities and resources proves paramount in establishing attainable aims. This requires thoughtful consideration of external factors and potential obstacles.
A critical component involves recognizing personal limitations and strengths. Focusing solely on perceived capabilities without accounting for challenges often leads to failure. Understanding your capacity enables roadmap creation aligned with abilities and fostering accomplishment.
Approaches for Task Decomposition
Large projects can feel intimidating. Breaking them into smaller, manageable steps makes them less daunting and more achievable. This incremental approach prevents overwhelm by focusing on individual components. Regular step assessment and adjustment maintains progress and motivation.
Planning and scheduling form essential decomposition elements. Detailed timelines with step deadlines enable progress tracking and necessary adjustments. This structured method promotes accountability and provides clear navigation paths. Consider incorporating time management techniques like the Pomodoro method for optimized focus.
Task prioritization by importance and urgency represents another valuable strategy. Identifying critical steps first establishes efficient workflows. Understanding task sequences enables effective process establishment.
Anticipating and Addressing Obstacles
Foreseeing potential challenges is crucial for expectation management and realistic goal-setting. Identifying possible obstacles enables solution development, preventing overwhelm and fostering preparedness. Proactive obstacle management maintains momentum toward objectives.
Effective strategies include anticipating challenges and brainstorming solutions. Creating contingency plans for setbacks provides safety nets and alternative pathways. This preparation enables flexibility and adaptation.
Communicating goals and expectations with others proves equally important. Sharing plans with colleagues or mentors creates accountability networks and valuable support. This dialogue ensures aligned expectations and early obstacle identification.
Regular progress evaluation and necessary adjustments represent key obstacle-overcoming elements. Periodic assessment identifies areas needing modification, keeping you on track. This allows timely course corrections ensuring goal achievement.
Effective stakeholder communication and collaboration are essential for obstacle navigation. Keeping all parties informed and involved fosters shared understanding and collective goal pursuit.