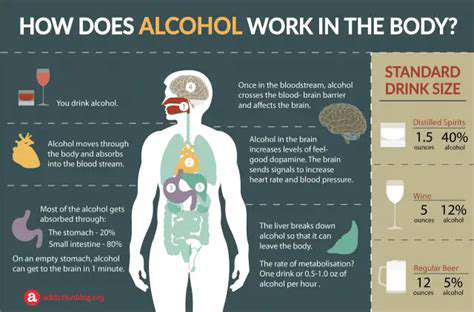
Alcohol's Stealthy Aftereffects
While that glass of wine might help you unwind initially, your body wages a silent battle against its toxic effects for hours afterward. The consequences creep up subtly - a dull headache upon waking, unexplained fatigue by midday, or unexpected irritability during meetings. These aren't coincidences but direct results of alcohol's biochemical warfare on your system.
Your body treats alcohol as poison from the first sip, triggering complex detoxification processes that drain energy and resources from other vital functions. This explains why even moderate drinkers often feel off the next day without understanding why.
Your Body's Water Crisis
Alcohol doesn't just make you thirsty - it hijacks your body's water distribution system. Each drink forces your kidneys to work overtime, flushing out not just alcohol byproducts but crucial electrolytes and minerals too. This creates a cellular drought where your brain actually shrinks temporarily from fluid loss, causing those pounding headaches.
The dehydration domino effect continues with muscle cramps, dry mouth, and that sandpaper feeling behind your eyes. What most people don't realize is that drinking water alongside alcohol only partially mitigates this - your body still loses more fluids than it can replace in real time.
Gut Rebellion
Your digestive system mounts a full-scale protest after alcohol exposure. The stomach lining becomes irritated, digestive enzymes get disrupted, and gut bacteria suffer collateral damage. This explains why breakfast might seem revolting the next morning, even if you didn't drink excessively.
Alcohol's inflammatory effects extend throughout the entire digestive tract, potentially causing everything from acid reflux to irregular bowel movements. The liver prioritizes alcohol metabolism over other functions, creating a metabolic traffic jam that backs up other digestive processes.
Brain Fog Warfare
That fuzzy feeling isn't just in your head - alcohol literally scrambles your neural networks. Neurotransmitters get thrown out of balance, neural pathways fire erratically, and your brain's cleanup crew works overtime removing alcohol-induced cellular debris. This explains why simple tasks feel challenging and why you might forget where you parked your car.
The cognitive hangover often lasts longer than the physical symptoms, with some studies showing impaired decision-making and reaction times up to 48 hours after drinking. This has serious implications for workplace performance and driving safety.
The Sleep Deception
While alcohol might knock you out faster, it sabotages sleep quality in multiple ways. It suppresses REM sleep (the mentally restorative phase), disrupts circadian rhythms, and increases nighttime wakefulness. You might sleep for 8 hours but wake feeling like you barely rested at all.
This sleep debt accumulates, contributing to next-day fatigue, poor concentration, and even weakened immunity. The vicious cycle continues as tiredness prompts cravings for more alcohol or caffeine to compensate.
Emotional Hangover
Alcohol's chemical rollercoaster doesn't just affect your body - it plays havoc with your emotions too. The initial euphoria gives way to neurotransmitter depletion, leaving many people feeling anxious or depressed the next day. This hangxiety can be particularly intense for those predisposed to mood disorders.
Compounding Damage
While one night of drinking might cause temporary issues, repeated exposure creates cumulative damage that becomes increasingly difficult to reverse. Liver cells scar, brain volume decreases, and cancer risks rise with each additional drink over time.
The body's remarkable resilience has limits - while it can recover from occasional overindulgence, chronic drinking pushes systems past their repair capacity. This explains why some effects become permanent in long-term heavy drinkers.
True wellness requires emotional equilibrium, especially when navigating alcohol's biochemical and psychological impacts. Maintaining stability becomes both more challenging and more crucial when alcohol enters the equation.
