Introduction to Head Pain Behind the Eyes
Common Causes of Head Pain Behind the Eyes
Head Pain Behind the Eyes can arise from a variety of sources. One of the most frequent culprits is tension headaches, which often manifest after prolonged periods of stress or concentration. These headaches may be accompanied by discomfort around the eyes, creating a feeling of pressure.
Sinus infections are another common reason for Pain behind the eyes. When the sinus cavities become inflamed and filled with mucus, they can put pressure on the surrounding areas, causing significant discomfort. This type of pain is often accompanied by other symptoms such as nasal congestion and facial swelling.
Migraines are well-known for causing intense pain that can radiate to the area around the eyes. These headaches often come with additional symptoms such as nausea and sensitivity to light and sound, making them particularly debilitating for those who suffer from them.
Eye strain is also a prevalent cause of pain behind the eyes. Extended screen time, reading in poor lighting, or not wearing prescription glasses can lead to discomfort. Eye strain usually resolves with proper rest and adjustments to visual habits.
Additionally, conditions such as high blood pressure and cluster headaches can result in pain behind the eyes. It is crucial to recognize these potential causes so individuals can seek appropriate treatment and management options.
Recognizing Symptoms Associated with Head Pain Behind the Eyes
Identifying the specific symptoms that accompany head pain behind the eyes can be essential for diagnosis. Aside from the primary pain itself, individuals may experience blurred vision or a sensation of pressure in their eye area.
Many people report accompanying symptoms like nausea or light sensitivity, particularly in migraine sufferers. Such symptoms can significantly affect daily activities, making it important to address them effectively.
Additionally, other sensations such as throbbing or pulsating pain may indicate the presence of a migraine, whereas a dull ache is often more characteristic of tension headaches.
Some individuals may encounter sinus-related symptoms, such as a feeling of fullness or pressure in the forehead and cheek area, which can exacerbate the pain felt behind the eyes.
Tracking these associated symptoms over time can help healthcare providers make a more accurate diagnosis and tailor treatment plans accordingly, ensuring relief for those affected.
Effective Solutions for Managing Pain Behind the Eyes
Managing pain behind the eyes requires a multi-faceted approach. For tension headaches, regular breaks and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and yoga, can significantly alleviate symptoms.
For sinus-related pain, staying hydrated and using saline nasal sprays can help reduce inflammation and relieve pressure. Over-the-counter decongestants might also provide temporary relief during acute bouts.
In cases of migraines, identifying and avoiding triggers—such as certain foods or stressors—can be beneficial. Medications specifically for migraine relief, along with lifestyle adjustments like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, are often recommended.
Eye strain can frequently be managed through proper ergonomics and screen usage practices. The 20-20-20 rule—looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes—can help reduce discomfort.
Lastly, regular consultations with healthcare providers can ensure that any underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure, are monitored and managed effectively, promoting overall eye and head health.
Common Causes of Head Pain Behind the Eyes
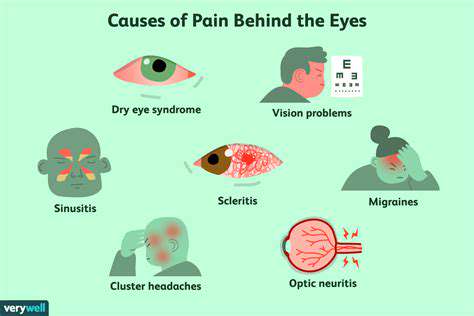
Sinusitis: A Major Culprit
Sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus cavities, is a common cause of pain located behind the eyes. This condition often occurs alongside cold or allergy symptoms, making it easy to overlook. When sinuses become swollen or infected, pressure builds up, leading to discomfort. This type of headache tends to worsen with certain movements or positions, such as bending over.
The pain can radiate to the forehead, cheeks, and eyes, contributing to a generalized feeling of heaviness. Treatment typically involves decongestants, nasal sprays, or antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present. Maintaining hydration can also aid in thinning mucus and relieving symptoms.
Chronic sinusitis can be particularly troublesome, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. Seeking medical advice is crucial for long-term relief and management strategies.
Preventative measures like staying away from allergens and practicing good hygiene can help reduce the frequency of sinusitis episodes.
Migraines: More than Just a Headache
Migraines are another prevalent source of head pain located behind the eyes. These severe headaches often present with throbbing pain, sensitivity to light, and nausea. They can last from a few hours to several days, severely impacting daily activities.
Migraine triggers vary from person to person, with common culprits including stress, specific foods, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. Understanding and identifying triggers is essential for effective management. Many people benefit from keeping a headache diary to track patterns and potential triggers.
Acute treatments include over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications, which can help alleviate symptoms during an attack. For chronic sufferers, preventive medications and lifestyle adjustments may be recommended to reduce the frequency of migraines.
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and cognitive behavioral therapy, can also be effective for some individuals in managing migraines.
Eye Strain: A Modern-Day Concern
In our increasingly digital world, eye strain has become a prevalent issue, contributing to pain behind the eyes. Prolonged screen time can lead to a condition often known as computer vision syndrome. Symptoms may include tired eyes, headaches, and blurred vision.
To combat eye strain, it’s advisable to follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away. Additionally, ensuring proper lighting and maintaining an appropriate monitor distance can help reduce symptoms. Regular eye exams can catch underlying issues early, ensuring that corrective lenses or other treatments are utilized.
Investing in blue light-blocking glasses is another option many people consider to alleviate eye discomfort from screens. While these glasses may not work for everyone, there’s evidence suggesting they can help some individuals reduce digital eye strain.
Implementing ergonomic practices in your workspace can make a significant difference in comfort and productivity, directly impacting overall eye health.
Tension Headaches: The Silent Discomfort
Tension headaches are characterized by a dull, aching pain and a sensation of tightness behind the eyes. They are often linked to stress, anxiety, or muscle tightness in the neck and shoulders. Unlike migraines, tension headaches tend not to be accompanied by nausea or sensitivity to light.
Identifying stressors and learning effective coping mechanisms, such as relaxation techniques and mindfulness, can greatly reduce the frequency of tension headaches. Regular physical activity and proper hydration can also play crucial roles in prevention and relief.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are often effective in managing the pain of tension headaches. However, if these headaches become chronic, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Integrating daily practices like stretching and maintaining good posture can also help alleviate tension and, consequently, lessen the likelihood of headaches forming.
Identifying Symptoms
Common Symptoms Associated with Pain Behind the Eyes
Pain behind the eyes can manifest in various ways, and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis. Commonly reported sensations include dull, throbbing, or sharp pain. Some individuals may experience discomfort that feels worse with movement or strain.
Another prevalent symptom is associated visual disturbances. This might include blurriness, sensitivity to light, or seeing halos around lights. These symptoms can significantly affect daily activities, making it essential to monitor their frequency and intensity.
Additionally, headaches often accompany this type of eye pain. These headaches can vary in severity and may be concentrated in the frontal or occipital regions. Many patients report that their headache aligns with the pain behind the eyes, which can complicate the overall understanding of their condition.
Fatigue and strain around the eyes are also common symptoms. Individuals might notice their eyes feeling heavy or fatigued, particularly after prolonged screen use or reading. This fatigue can heighten discomfort, leading to a vicious cycle of pain and strain.
Finally, some patients may experience accompanying symptoms, such as dizziness or nausea. These symptoms can exacerbate the feeling of eye pain and might suggest underlying issues that require medical attention.
Possible Causes of Pain Behind the Eyes
There are several potential causes for pain located behind the eyes, which can range from benign to more serious conditions. One of the most common culprits is eye strain, particularly from prolonged use of digital devices. With the rise of remote work and online learning, this issue has become increasingly prevalent.
Sinusitis is another significant cause of discomfort behind the eyes. Inflammation of the sinus cavities can create pressure that radiates into the eye region, resulting in both pain and discomfort. This condition is often accompanied by other symptoms such as nasal congestion and facial pain.
Cluster headaches are known for causing severe pain behind the eyes, characterized by intense episodes that can last for several weeks. These headaches often occur in cyclical patterns and are more common in men than in women.
Migraine sufferers may also experience pain behind the eyes as part of their headache episodes. Migraines are typically accompanied by auras, nausea, and increased sensitivity to light, making them particularly debilitating.
Finally, more serious medical conditions, such as glaucoma or tumors, can lead to pain behind the eyes. These conditions can threaten vision and overall health, making it imperative to seek medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when to seek medical attention is essential for anyone experiencing pain behind the eyes. If the pain is sudden and severe, particularly if it is accompanied by vision loss or neurological symptoms, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Additionally, persistent symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter pain relief or self-care measures warrant a doctor's visit. This includes pain that disrupts daily activities or sleep, signaling a need for professional evaluation.
Patients should also be cautious if their eye pain is accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, chills, or severe nausea. These symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires urgent evaluation.
Any changes in vision, such as blurriness or seeing halos, should be taken seriously as they can be signs of significant health issues. Seeking timely advice can help address potential complications before they worsen.
Lastly, if recurring headaches or eye pain are affecting quality of life, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for further investigation and management options available.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
There are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate pain behind the eyes. One of the simplest measures is to take regular breaks from screen time. Following the 20-20-20 rule can be beneficial: every 20 minutes, focus on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
Applying a warm compress to the eyes can also provide relief. This method helps relax strained muscles and improve circulation, often resulting in significant comfort. Alternatively, cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb the area, which might be helpful depending on the underlying cause.
Staying hydrated is another crucial lifestyle change. Dehydration can exacerbate headaches and eye strain, so drinking adequate water throughout the day is essential for maintaining overall health.
Practicing good ergonomics when working on a computer can also reduce the strain on the eyes. This includes adjusting screen height, ensuring proper lighting, and using blue light filters when necessary.
Lastly, engaging in relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can alleviate stress and tension, which may contribute to eye pain. Regular physical activity can also promote better circulation and reduce the likelihood of headaches.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
When home remedies and lifestyle changes fail to relieve pain behind the eyes, medical treatments may be necessary. Healthcare providers may prescribe medications that are quick to relieve pain, such as analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs. Some patients may respond well to over-the-counter options, while others might require stronger prescriptions.
For those suffering from migraines or cluster headaches, specific medications known as triptans might help ease symptoms. These medications are designed to target headache pain and can be effective in managing acute attacks.
If the pain behind the eyes is due to an underlying condition such as sinusitis, doctors may prescribe decongestants or antibiotics as appropriate. Effective treatment can help reduce sinus pressure and alleviate associated pain.
Physical therapy can also be beneficial, especially for those experiencing tension-related discomfort. Therapists can provide exercises and techniques to strengthen the muscles around the eyes and neck, relieving strain over time.
In some cases, ophthalmologists might recommend corrective lenses or suggest surgical options for conditions like glaucoma. Regular check-ups can help monitor eye health and prevent serious complications.
Effective Remedies and Treatment Options
Understanding the Causes of Pain Behind the Eyes
Pain behind the eyes can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from strain to serious medical conditions. It's crucial to Identify the underlying cause to effectively address the discomfort. Common causes include tension headaches, sinusitis, and visual strain from prolonged screen time.
In many cases, the tension and pressure build-up in the head can radiate pain to the areas behind the eyes. This can lead to a feeling of discomfort that may worsen throughout the day. Identifying triggers, such as stress or eye strain, can help in finding the right treatment approach.
For some individuals, conditions like migraines or cluster headaches can cause severe pain that localizes behind the eyes. Understanding these various causes helps in developing a personalized treatment plan for relief.
Home Remedies for Relieving Eye Pain
There are several effective home remedies that can help alleviate pain behind the eyes. Simple practices include applying a cool compress to the forehead and eye area, which can help reduce inflammation and soothe discomfort. Regular breaks from screens are also vital.
Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga can significantly aid in easing tension headaches. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help keep headaches at bay, as certain foods may trigger pain for some individuals.
Moreover, ensuring adequate sleep and managing eye strain through proper lighting and screen filters can make a notable difference in reducing pain behind the eyes.
Over-the-Counter Medications and Treatments
When home remedies are not sufficient, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide relief for pain behind the eyes. Common options include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or aspirin, which can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Topical treatments, including pain-relief gels or creams, can also be applied to the forehead or temples to provide localized relief. It's essential to follow dosage instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
Additionally, if tension headaches are the culprit, relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes can complement the use of these medications for a more effective approach to pain management.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of pain behind the eyes are benign, some symptoms warrant a visit to a healthcare provider. If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as vision changes, it’s vital to seek medical attention. Early intervention can prevent more serious health issues.
Other warning signs include nausea, vomiting, or aura effects, which can indicate more serious underlying conditions such as migraines or sinus infections. Keeping a symptom diary can also help clarify patterns and triggers that can aid your healthcare provider in making an accurate diagnosis.
Overall, recognizing the signs that necessitate professional help can lead to timely treatment and improved overall health outcomes.