Introduction to Lower Left Head Pain
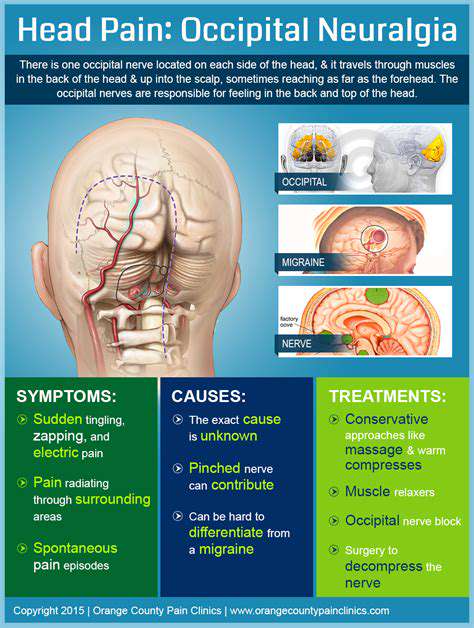
The Anatomy of Head Pain
Understanding head pain, especially in the lower left region, requires a grasp of the complex structures present in the human head. From muscles and nerves to blood vessels and sinuses, each component plays a role in how pain is perceived.
The lower left section of the head involves various anatomical structures, including the left temple, jawline, and portions of the neck. Any disturbance in these areas can lead to discomfort and pain, indicating that various medical issues could be at play.
In addition to the skeletal and muscular elements, the cranial nerves, such as the trigeminal nerve, are crucial for sensation in the face. When these nerves are irritated or compressed, it can manifest as localized head pain.
Thus, a thorough understanding of the anatomical components involved is vital for diagnosing and treating lower left head pain. Gaining this insight helps both patients and healthcare providers formulate effective treatment strategies.
Common Causes of Lower Left Head Pain
The origins of lower left head pain can be multifaceted, ranging from tension headaches to more serious medical conditions. Tension headaches, one of the most prevalent forms, can cause discomfort in any region of the head, particularly on one side.
Another common cause includes migraines, which often present with intense throbbing usually localized on one side. Migraines can be exceptionally debilitating, frequently accompanied by symptoms such as light sensitivity and nausea, leading to further complications.
Cluster headaches, although less common, also present strong pain that often concentrates on one side of the head, typically the lower left. These headaches may follow a cyclical pattern, making them unique and challenging to treat.
Moreover, dental issues like tooth infections or a misaligned jaw can also lead to lower left head pain, making it essential for individuals to recognize potential dental links to their discomfort.
Diagnosis Procedures for Head Pain
Diagnosing lower left head pain typically involves a comprehensive assessment, including medical history and a physical examination. Doctors often ask patients detailed questions about the nature, duration, and intensity of the pain.
In some cases, imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans may be necessary to rule out serious conditions like tumors or bleeding within the brain. These diagnostic tools provide invaluable insights about the underlying issues affecting the patient.
Additionally, blood tests can be conducted to evaluate any systemic causes, such as infections or inflammatory conditions. A thorough and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of head pain.
By utilizing a combination of patient history, physical exams, and advanced imaging techniques, healthcare providers can achieve a more precise understanding of the causes behind lower left head pain, ensuring appropriate interventions are applied.
Solutions and Treatments for Lower Left Head Pain
Once a diagnosis is established, various treatment options are available depending on the cause of the lower left head pain. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are often effective for relieving minor pains.
For individuals suffering from tension or migraine headaches, preventive medications may be prescribed, aiming to reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes. These could include beta-blockers or certain antidepressants, tailored to the patient's needs.
In addition, non-pharmacological treatments, such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and relaxation techniques, have gained popularity for managing chronic head pain. Integrating these holistic approaches can often enhance traditional medical treatments and improve overall well-being.
Ultimately, creating a personalized treatment plan that considers the patient's condition, lifestyle, and preferences is essential for effectively managing lower left head pain and improving quality of life.
Common Causes of Lower Left Head Pain
Muscle Tension and Strain
Muscle tension in the neck and shoulders is one of the most common culprits for lower left head pain. This tension can often result from poor posture, prolonged screen time, or even emotional stress. When muscles become tight, they can lead to referred pain in areas like the lower left side of the head and can manifest as discomfort that may come and go.
Addressing muscle tension typically involves identifying the triggers. Simple changes in daily habits, such as adjusting the height of your computer screen or practicing relaxation techniques, can help alleviate the pressure. Additionally, regular stretching and strengthening exercises can promote improved posture and reduce the likelihood of strain on the surrounding muscles.
Sinus Issues
Sinus problems, particularly sinusitis, can lead to localized pain, often felt in the lower left area of the head. This condition occurs when the sinus cavities become inflamed or infected, causing pressure and discomfort. Symptoms may include facial pain, nasal congestion, and headaches, which can be quite disruptive to daily life.
To tackle sinus-related pain, it’s essential to keep the nasal passages clear. Home remedies like steam inhalation, saline nasal sprays, and staying hydrated can be beneficial. In some cases, over-the-counter medication or prescription treatments may be necessary to alleviate the ensuing inflammation and assist in restoring sinus health.
Neurological Conditions
Lower left head pain can also be a sign of underlying neurological issues such as migraines or nerve compression. Migraines may present with severe, throbbing pain that could be accompanied by nausea, visual disturbances, or sensitivity to light and sound. If the pain is recurrent and debilitating, it may warrant a visit to a healthcare professional for evaluation.
Managing neurological-related pain often requires a multifaceted approach. Identifying triggers, whether they be dietary, environmental, or stress-related, can play a crucial role in prevention. Medication prescribed by a healthcare provider can also assist in pain relief, while lifestyle adjustments like regular exercise and adequate sleep can contribute to an overall reduction in headache frequency.
Dental Issues
Dental problems, such as tooth decay, gum disease, or issues with the jaw joint (TMJ) can also contribute to lower left head pain. These dental concerns often manifest as localized pain that may radiate to the nearby areas, including the head. A common symptom associated with these problems is a dull ache that becomes more pronounced during chewing or biting.
If you suspect dental issues may be the culprit of your pain, it’s important to consult a dentist. Proper diagnosis and treatment are key in alleviating pain caused by dental problems. Treatment may include fillings, crowns, or even orthodontic evaluation to address alignment problems that could be contributing to strain in the jaw and lower head region.
Effective Treatments and Solutions

Understanding the Root Causes
Numerous factors can contribute to lower left head pain, including tension, migraines, and various medical conditions. Identifying the precise nature of the pain is vital for effective treatment. Consultation with healthcare professionals can yield important insights into the underlying causes.
Additionally, lifestyle choices such as poor posture, lack of sleep, and stress can exacerbate these issues. Addressing these contributing factors is essential in managing headaches effectively and improving overall health.
Medical Treatments Available
For persistent lower left head pain, several medical treatments may be recommended by healthcare providers. Common options include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, as well as prescription medications for chronic conditions. Effective medical treatment can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches.
In some cases, botox injections and nerve blocks are also considered for severe headaches that do not respond to standard medications. These treatments can provide long-term relief and help patients return to a normal lifestyle.
Alternative Therapies to Consider
Many individuals seek alternative therapies as a complement to traditional medical treatments for lower left head pain. Techniques such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy can alleviate tension and improve circulation. These holistic approaches are valuable for promoting relaxation and reducing pain.
Lifestyle Changes That Help
Making changes to daily routines and habits can significantly impact the frequency and severity of lower left head pain. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate hydration are integral to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Incorporating stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation can also be beneficial.
Additionally, it's essential to establish a regular sleep schedule and create a conducive sleep environment. Ensuring quality sleep can prevent headaches caused by fatigue and stress, leading to better management and reduction of head pain episodes.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when to consult a healthcare professional is crucial for effectively managing lower left head pain. If headaches become increasingly frequent or intense, or are accompanied by other unusual symptoms, immediate medical attention is warranted. Taking proactive steps can prevent complications and promote timely treatment.
Moreover, individuals should be aware of the warning signs of more serious conditions. Symptoms such as visual disturbances, confusion, or severe neck stiffness require urgent care and should never be ignored, as they may indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding the Severity of Symptoms
Identifying the severity of symptoms associated with lower left head pain is crucial. If the pain you experience is sudden, intense, or accompanied by other alarming signs such as confusion, difficulty speaking, or visual disturbances, it's important to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt intervention.
Additionally, if the pain persists or worsens over time, it may indicate an evolving health issue. Chronic headaches or a shift in pain patterns can signal problems such as migraines, tension headaches, or even issues related to the cervical spine. Early evaluation by a healthcare professional can resolve concerns and potentially prevent the condition from escalating.
Identifying Accompanying Symptoms
When lower left head pain is accompanied by other symptoms, this can greatly influence the decision to seek medical care. For example, experiencing nausea, vomiting, or light sensitivity alongside head pain could suggest a migraine attack, warranting a visit to a healthcare provider for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Furthermore, if the head pain is accompanied by neurological symptoms such as weakness, numbness in the limbs, or seizures, these could be indicators of serious conditions like stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). In such cases, prompt medical evaluation is critical to receiving timely and effective treatment.
Chronic vs. Acute Pain: Knowing When to Act
Understanding the difference between chronic and acute pain is essential when assessing whether to seek medical attention for lower left head pain. Acute pain may arise suddenly and can be intense but is often resolved with appropriate care. In contrast, chronic pain lasts for extended periods and may require more in-depth investigation to determine its cause.
If you find yourself needing over-the-counter medications frequently or if the pain disrupts your daily activities, it is time to consult a healthcare professional. A thorough assessment can help identify underlying conditions contributing to the pain, allowing for targeted treatment that can enhance your quality of life.
Considering Risk Factors for Serious Conditions
Certain risk factors can elevate the urgency of seeking medical attention for head pain. Individuals with a history of high blood pressure, blood clotting disorders, or those who have recently experienced head trauma should be particularly vigilant. These factors can predispose individuals to more serious issues, including hemorrhagic strokes or aneurysms, requiring immediate assessment.
Moreover, lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle may amplify the risk of developing significant health issues linked to head pain. Being aware of your personal risk factors and promptly addressing unusual symptoms can lead to early detection and more effective treatment options, ultimately improving your health outcomes.