What is Stabbing Pain?

Understanding the Nature of Stabbing Pain
Stabbing pain is often described as a sharp, intense sensation that can occur suddenly. This type of pain can feel like a knife piercing through the body, making it quite distinct from other pain forms.
It may arise from various conditions, affecting different parts of the body, such as the chest, abdomen, or even limbs. Recognizing where the stabbing pain originates is crucial to determine its cause.
Patients often report that the pain can vary in intensity and duration. It might come in fleeting episodes or persist, leading to significant discomfort and distress.
In some cases, stabbing pain can be acute, meaning it comes on suddenly and aggressively, while in others, it can be chronic, lingering over time.
Understanding the context and features of stabbing pain can aid both patients and healthcare providers in diagnosing and treating the underlying issues.
Common Causes of Stabbing Pain
Stabbing pain can result from numerous medical conditions, including nerve-related issues like neuropathy. This condition can cause sharp, shooting pains, particularly in the extremities.
Another frequent cause is injury or trauma, where physical damage to muscles, ligaments, or organs results in intense pain. Consulting a healthcare professional after an injury is vital to address any severe underlying issues.
Some gastrointestinal problems, such as appendicitis or gallstones, can also produce stabbing sensations in the abdomen. These cases often require immediate medical attention due to their potential severity.
Stabbing pain might also be associated with conditions affecting the heart or lungs, such as pericarditis or a pulmonary embolism. Early identification of symptoms can be life-saving.
Additionally, mental health issues, such as anxiety or panic attacks, can manifest physical symptoms, including stabbing pain, making a comprehensive approach to care essential.
Treatment Options for Stabbing Pain
Addressing stabbing pain requires a multifaceted approach, starting with an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare provider. Treatment strategies may vary significantly based on the underlying cause.
Medications, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs, are often prescribed to manage symptoms effectively. In some cases, more specialized treatments like anticonvulsants or antidepressants may be necessary.
Physical therapy can also play a crucial role in rehabilitation, particularly for pain resulting from injuries. Strengthening and stretching exercises can help alleviate some discomfort.
Alternative treatments, including acupuncture and chiropractic care, have proven beneficial for some individuals experiencing stabbing pain. These methods can provide relief and promote overall well-being.
Lastly, lifestyle modifications, such as stress management techniques and healthy diet choices, can aid in managing chronic conditions that cause stabbing pain, enhancing quality of life.
Common Causes of Stabbing Pain
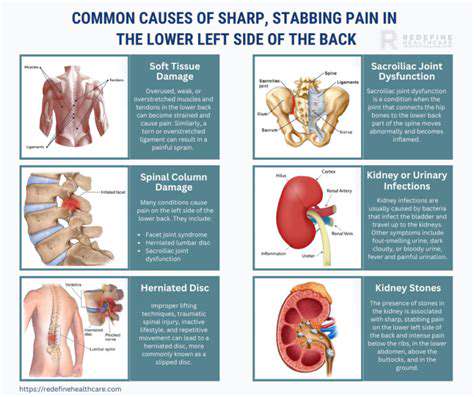
Understanding the Types of Stabbing Pain
Stabbing pain can manifest in various ways depending on its source.
It is often described by patients as a sharp, intense sensation that comes on suddenly.
This type of pain can be localized or diffuse, affecting larger areas of the body.
Identifying the exact location and nature of the pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Common areas where stabbing pain is experienced include the chest, abdomen, and back.
Medical Conditions Associated with Stabbing Pain
A range of medical conditions can lead to stabbing pain.
For instance, conditions like pancreatitis often result in severe, stabbing abdominal pain.
In some cases, stabbing pain may indicate more serious issues, such as heart problems or internal injuries.
It's essential to seek medical advice if you experience stabbing pain, especially if it is persistent or severe.
Pulmonary issues, such as a pulmonary embolism, can also manifest as acute stabbing pain in the chest area.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stabbing Pain
Management of stabbing pain often begins with addressing its underlying cause.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort in many cases.
In more severe situations, prescription medications or therapies may be required to manage the pain effectively.
Physical therapy and lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in reducing chronic pain.
Additionally, techniques such as acupuncture and mindfulness meditation can provide relief for some individuals.
Identifying Symptoms Associated with Stabbing Pain
Common Symptoms of Stabbing Pain
Stabbing pain is often described as a sharp, intense sensation that can occur suddenly. It may feel as though something is piercing through the body, which can create a sense of urgency or alarm in the affected individual. This pain can vary in intensity and can be localized to specific areas or spread through different parts of the body.
Many people also report accompanying symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation in the affected area. These symptoms can further complicate the experience of stabbing pain, making it difficult to pinpoint the cause or determine the appropriate treatment. Understanding that these associated sensations can provide crucial information regarding the underlying issue is vital for effective management.
In some cases, stabbing pain may be accompanied by symptoms of anxiety or distress, particularly if the pain is severe or recurrent. Individuals may find themselves in a perpetual state of worry about when the next episode will occur, which can negatively impact their overall quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when stabbing pain requires medical intervention is important for ensuring timely and effective treatment. If the pain is persistent, increases in intensity, or occurs alongside concerning symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, or loss of consciousness, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Additionally, if stabbing pain is associated with signs of infection (such as fever or swelling), uncontrolled bleeding, or traumatic injury, immediate evaluation is warranted. These symptoms can indicate serious health issues that need prompt care to prevent further complications.
Even if the stabbing pain is intermittent or mild, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional if it disrupts daily activities or sleep. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and minimize the risk of developing chronic pain conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing Severe Symptoms
It is crucial to be aware of severe symptoms that accompany stabbing pain. These may include intense, persistent pain, difficulty breathing, or loss of consciousness. If the stabbing pain is sudden and severe, it is essential to seek immediate medical help.
Another indicator that medical attention may be necessary is if the pain is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or changes in vision. These could signify a more serious underlying condition that needs urgent treatment. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to serious complications.
Moreover, if you notice any signs of infection, such as fever or swelling in the area of pain, it's important to consult a doctor. These symptoms may suggest that the issue is not benign and requires intervention for proper management.
Understanding Your Medical History
Your medical history plays a significant role in identifying the necessity for medical intervention. If you have a history of heart disease, it is advisable to seek medical advice if you experience stabbing pain, especially in the chest area. Pre-existing conditions can significantly influence the seriousness of your symptoms.
Additionally, if you are on medication or have undergone recent surgeries, it's vital to inform your healthcare provider when reporting stabbing pain. Changes in medication or post-surgical complications can manifest as unexpected pain, which may require a different form of treatment.
Regular check-ups can also help in monitoring any potential issues that could lead to sudden stabbing pain. Being proactive about your health can greatly contribute to early detection and successful treatment of any underlying problems.
Effective Solutions and Treatments
Understanding the Causes of Stabbing Pain
Stabbing pain can be a perplexing and often alarming symptom, as its sudden onset may lead to significant distress. It's essential to understand that this type of pain can arise from a variety of causes, both acute and chronic. Musculoskeletal issues, such as muscle strains or ligament injuries, can produce sharp sensations that may come and go with movement.
Another common cause of stabbing pain is nerve-related conditions, such as sciatica or neuropathy. When nerves are compressed or damaged, they can send erratic pain signals to the brain, which are often described as stabbing or stabbing-like sensations. This can happen due to herniated discs or certain systemic diseases.
In some cases, stabbing pain can be linked to underlying health conditions, such as gastrointestinal issues. Conditions like gallstones or pancreatitis can manifest with acute pain in the abdominal region, which some individuals might describe as a stabbing feeling. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for effective treatment.
Infections, such as shingles, can also lead to stabbing pain. The varicella-zoster virus, which causes shingles, can create sharp, burning pain that may precede a rash. It's important to consider the timing of the pain and any accompanying symptoms to identify the root cause accurately.
Effective Treatments and Management Strategies
Dealing with stabbing pain effectively often requires a multi-faceted approach. Initially, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis; they may recommend imaging studies or blood tests to determine the underlying cause. Once diagnosed, treatment options vary widely based on the root of the problem.
For acute pain management, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief. Ice or heat therapy can also be beneficial; applying ice reduces inflammation, while heat can alleviate muscle tension. It's important to follow the guidelines for using these methods safely to avoid further injury.
Physical therapy is another critical component of managing stabbing pain, especially when it stems from musculoskeletal issues. A qualified physical therapist can develop a tailored exercise program that strengthens affected muscles, increases flexibility, and mitigates pain over time.
If the pain is chronic and does not respond to conventional treatments, alternative therapies may be considered. Techniques such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, or even mindfulness meditation can offer relief. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting new treatment modalities to ensure they align with your specific condition and overall health.