慢性疾病与健康风险之间的关系
慢性疾病对身体的影响
慢性疾病,如糖尿病、心脏病和自身免疫性疾病,会显著改变身体正常运作的能力。这些疾病常常导致一系列并发症,这些并发症可能会加重症状并降低生活质量。例如,糖尿病患者可能会出现神经病变,影响四肢和整体行动能力。
此外,慢性疾病通常导致慢性炎症,这可能增加患上其他健康问题的风险。炎症在各种疾病中扮演着关键角色,从关节炎到心血管问题,突显了健康问题的相互关联性。
此外,慢性疾病患者可能面临更高的心理健康问题风险,如抑郁症和焦虑症。慢性疾病的持续管理可能会导致情感压力,加重日常面临的身体挑战。
理解慢性疾病的全面影响对于患者和医疗提供者来说都至关重要。妥善管理这些疾病对于降低风险和改善整体健康结果是必不可少的。
与慢性疾病相关的风险因素
几个风险因素会促成慢性疾病的发展和进展。生活方式选择,如不良饮食、缺乏锻炼和吸烟,是导致严重健康并发症的重要因素。这些习惯不仅提高了患慢性疾病的风险,还使已经确诊患者的管理变得复杂。
遗传因素在确定个体对慢性疾病的易感性方面也发挥着重要作用。家族病史可能会增加患高血压或2型糖尿病等疾病的可能性,这使得个人意识到家庭健康历史至关重要。
社会经济因素是另一个关键因素,因为医疗保健、教育资源和社区支持的获取可能显著影响健康结果。较低的社会经济地位通常与获取营养食物和医疗服务的机会有限有关,进一步加剧了慢性疾病的风险。
通过教育、生活方式改变和可获得的医疗资源来应对这些风险因素,可以帮助降低与慢性疾病相关的并发症,促进更健康的人口。
管理慢性疾病的策略
有效管理慢性疾病需要多方面的方法。鼓励患者采用以全食、果蔬为主的均衡饮食,以支持整体健康并对抗炎症。营养教育在帮助个人做出更健康饮食选择方面发挥着重要作用。
定期身体活动也是管理慢性疾病的关键。锻炼可以改善心血管健康,帮助体重管理,并改善心理健康。每周进行至少150分钟的中等强度锻炼可以为慢性疾病患者带来显著益处。
个人和专业支持系统可以在管理慢性疾病方面提供宝贵的帮助。与医疗提供者、支持小组和心理健康专业人士联系可以促进更好的健康管理和情感支持。
最后,持续监测和积极管理健康可以带来改善的结果。利用健康追踪应用和可穿戴设备等技术,使患者能够了解自己的健康状况,从而在并发症出现时进行更及时的干预。
生活方式选择的作用

饮食对健康的影响
营养在维持整体健康和管理潜在疾病中起着关键作用。均衡饮食可以帮助预防慢性病的发展。 富含水果、蔬菜、全谷物和瘦蛋白的食物有助于改善健康结果。相反,高加工食品、糖和不健康脂肪的饮食可能加重现有健康问题。
此外,某些饮食模式与特定的健康状况有关。例如,高钠饮食可能导致高血压,而过量摄入糖与糖尿病相关。理解饮食选择与健康之间的关系可以使个人能够做出明智的决定。
此外,营养对那些已有健康状况的人至关重要。根据个人的健康状况量身定制饮食选择可以显著影响疾病管理。咨询注册营养师可以提供有关有效饮食策略的个性化指导。
总之,养成更健康的饮食习惯可以作为许多潜在健康状况的预防措施和治疗方法,最终提升个人的生活质量。
定期锻炼的重要性
身体活动是管理健康的另一个关键因素。参与规律的锻炼可以显著降低与各种健康状况相关的风险。它有助于增强心血管系统、调节血糖水平和维持健康体重。
此外,锻炼通过减轻焦虑和抑郁的症状来促进心理健康。即使是少量的身体活动,融入日常生活中,也可以随着时间的推移带来显著的健康益处。找到令人愉快的锻炼方式可以使保持一致更加容易。
对于已有健康状况的人,选择适合其能力和医疗建议的活动至关重要。通常可以对不同健身水平进行适应和修改。定期与医疗提供者进行沟通可以帮助确保锻炼的安全性。
最终,把身体活动作为健康生活方式的一部分优先考虑,对于预防和管理慢性健康状况至关重要。
压力管理的作用
慢性压力可能对身体健康产生负面影响,加重心脏病和糖尿病等潜在疾病。因此,压力管理技术是整体健康方法的重要组成部分。正念、冥想和深呼吸练习等方法可以有效降低压力水平。
参与爱好和愉快的活动也有助于改善心理健康。这些积极的出口可以为日常压力提供必要的分散注意力,并促进放松。将定期放松时间融入日程可以促进更好的压力管理。
此外,社会支持在管理压力中扮演着关键角色。与朋友和家人保持健康的关系可以为个人提供应对压力的缓冲。参与支持小组还可以创建一种社区感和共同理解。
总之,优先考虑压力管理不仅对心理健康有益,而且对有效管理潜在健康状况至关重要。
睡眠对健康结果的影响
优质睡眠通常被忽视,但在整体健康中扮演着重要角色。睡眠不足可能导致各种健康并发症,包括免疫力减弱和慢性病易感性增加。优先考虑良好的睡眠卫生对维持最佳健康至关重要。
建立规律的睡眠时间表和营造宁静的睡眠环境可以大大提高睡眠质量。限制就寝前的屏幕时间并保持放松的临睡例行可以促进更深、更恢复性的睡眠。此外,处理潜在的睡眠障碍对那些难以获得高质量休息的人至关重要。
此外,充足的睡眠支持有效的压力管理和情绪调节,从而促进更好的健康结果。睡眠障碍可能导致压力水平升高,加剧负面健康影响的循环。因此,专注于改善睡眠可以为个人的身体和心理健康带来广泛的益处。
最终,认识到睡眠在全面健康策略中的重要性对于那些希望有效管理健康的个人至关重要。
常见潜在疾病及其并发症
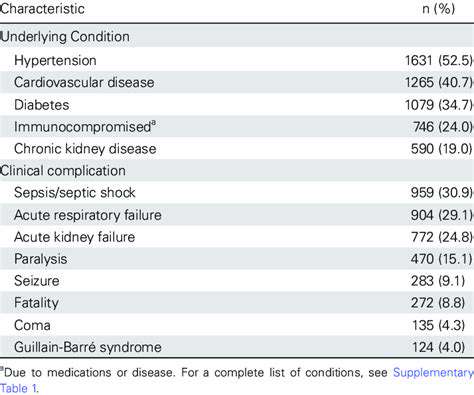
心血管疾病
心血管疾病,如心脏病和高血压,显著影响整体健康,并可能导致严重的并发症。有既往心脏病史的个体面临心脏病发作、中风和心力衰竭的风险更高。这些疾病通常需要严格管理,并可能使任何其他出现的医疗问题复杂化。定期体检和健康的生活方式对于有心血管问题的人至关重要,以降低风险。
此外,心血管疾病与其他健康并发症之间的相互作用可能相当复杂。例如,高血压可能导致肾脏损害,进一步复杂化个人的健康状况。了解这种关系有助于制定有效的治疗方案。因此,患者应与医疗提供者密切合作,以监测他们的心血管健康并遵循规定的干预措施。
教育患者识别心脏病恶化的迹象和症状至关重要。及时识别这些迹象可以促使及时干预,防止严重后果。意识和教育是有效管理心血管风险的关键组成部分。除了药物,饮食、锻炼和压力管理等生活方式的改变同样发挥着重要作用。
总之,心血管疾病是一个重要的潜在病症,具有深远的影响。有效的管理对于避免并发症和提高生活质量至关重要。通过优先考虑心血管健康,个人可以减少风险,过上更充实、更健康的生活。
糖尿病及其并发症
糖尿病是一种慢性病,如果管理不当可能导致严重并发症。最常见的并发症包括心血管问题、神经损伤和肾脏问题。有效的血糖管理对预防这些并发症和维持整体健康至关重要。这包括定期监测血糖水平和遵循规定的药物治疗。
例如,失控的糖尿病可能导致糖尿病神经病,这会导致四肢的疼痛和麻木。这种状况不仅影响行动能力,还可能导致严重感染,可能需要截肢。肾脏疾病是糖尿病可能引发的另一个并发症,需要密切监测肾功能。
除了医疗管理,饮食选择在糖尿病的预防和控制中扮演着关键角色。鼓励患者 adopt 一种低糖而富含全谷物、水果和蔬菜的均衡饮食。定期锻炼对于维持健康的血糖水平和预防并发症也至关重要。
最后,糖尿病患者必须与医疗团队密切合作,制定综合的护理计划。这包括定期检查,以评估和管理任何新出现的并发症。通过了解糖尿病相关的潜在风险,患者可以采取积极措施来保护他们的健康。
呼吸系统疾病及其影响
呼吸系统疾病,如哮喘和慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD),对整体健康构成重大风险,并可能因其他潜在疾病而加重。这些疾病往往导致发病率增加,并可能严重影响日常生活。患有呼吸问题的患者可能会感到呼吸困难,从而限制身体活动并影响心理健康。
呼吸系统疾病带来的并发症还包括反复感染和呼吸衰竭。哮喘患者可能发现其病情因过敏原和污染物加重,导致频繁住院。COPD患者面临呼吸道感染的高风险,这可能危及生命。
此外,管理呼吸系统疾病通常需要多方面的方法,包括药物治疗、生活方式改变和触发因素的避免。患者需要制定个性化的行动计划,以满足他们的具体需求和触发因素。与医疗提供者的定期跟进对于监测肺功能和必要时更新治疗计划至关重要。
教育对于呼吸系统疾病患者理解他们的疾病并有效管理至关重要。自我管理策略,如正确的吸入器使用技巧和识别恶化早期迹象,使患者能够掌控他们的健康。通过积极应对呼吸系统疾病,患者可以显著改善生活质量。
肥胖及其相关风险
肥胖是一种重要的潜在健康状况,可能导致大量严重并发症。它与糖尿病、心血管疾病和某些类型癌症密切相关。解决肥胖问题对于降低这些并发症的风险和提高整体健康至关重要。有效的体重管理策略应包括饮食和生活方式的调整。
肥胖带来的并发症不仅仅是身体上的;它们还包括心理健康问题,如焦虑和抑郁。面临肥胖的人可能会遭受污名和歧视,从而进一步加重其心理负担。持续的支持和咨询是有效肥胖管理的重要组成部分。
医疗提供者在指导患者迈向健康生活方式方面发挥着重要作用。这包括制定针对具体目标和可持续改变的量身定制的减肥计划。定期体育活动和均衡营养是实现和维持健康体重的基础。
总之,肥胖的后果超出了外观。它是多种疾病的重要风险因素,应通过包含教育、生活方式变更和医疗支持的全面方法来解决。通过优先考虑体重管理,个人可以朝着更健康的未来迈出重要一步。
心理健康障碍及其后果
心理健康障碍,如抑郁症和焦虑症,可以对个体的身体健康和整体幸福感产生深远影响。这些状况常常与身体疾病共存,并可能使治疗过程复杂化。解决心理健康问题对于实现整体健康结果至关重要。未能管理心理健康问题可能导致对医疗方案的遵循减少以及健康结果恶化。
研究表明,患有心理健康障碍的个体更容易发展出慢性疾病,如心脏病和糖尿病。因此,医疗提供者在常规医学评估中评估心理健康至关重要。将心理健康护理融入整体健康管理中可以显著改善患者的结果。
心理健康障碍的有效治疗选择包括治疗、药物和生活方式的变化。患者应该感到被赋予权力去寻求帮助,并参与各种可以改善其心理健康的干预措施。此外,制定应对策略和建立支持网络可以促进康复。
最后,提高社区对心理健康的意识至关重要。减少污名和教育可以鼓励个体提前寻求帮助并参与预防措施。增加心理健康问题的可见性将最终导致为受影响者提供更全面的护理。
定期健康筛查的重要性
预防措施以早期识别健康问题
定期健康筛查在未发展成严重疾病之前识别潜在健康问题方面发挥着至关重要的作用。这些筛查可以检测到糖尿病、高血压和某些癌症等疾病的早期迹象。
通过进行例行检查,个人可以与医疗服务提供者合作,制定个性化的预防策略。这些策略可能包括生活方式的改变、药物治疗或对特定健康指标的更密集监测。
早期发现通常会导致更有效的治疗选择和更好的预后。例如,在筛查过程中发现高血压,可以及时进行干预,从而预防心脏病。
在许多情况下,筛查测试可以以最小的不适和时间承诺完成,使大多数人都能接受。这种便利性鼓励更多个人关注自己的健康,并安排定期检查。
此外,许多健康保险计划覆盖常规筛查,使其对大部分人群在经济上可行。这种覆盖帮助消除了获得重要预防护理的障碍。
提高健康风险的认知和理解
定期健康筛查有助于个人更好地意识到自己的健康状况以及与潜在疾病相关的任何风险。这种意识可以增强个人掌握自己健康的能力,并做出明智的决定。
医疗服务提供者通常利用筛查的机会教育患者,了解与家族史或生活方式选择相关的各种健康风险。理解这些风险使患者能够在日常生活中实施必要的改变。
此外,筛查可以促进患者与医疗服务提供者之间就可能被忽视的担忧和症状进行开放的讨论。这种对话对于改善医疗体验至关重要。
鼓励定期筛查的文化可以对公共健康产生更广泛的影响,因为更高的早期发现率可以减轻社会的整体疾病负担。
最后,理解筛查的重要性可以鼓励患者积极主动而非被动应对自己的健康。培养这种心态有利于个人过上更长、更健康的生活,并促进整体健康社区的形成。