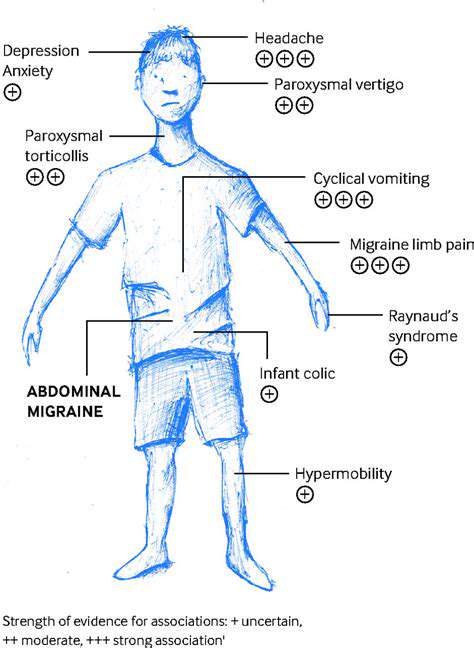
ما هو الصداع البطني عند الأطفال؟
ما الذي يسبب الصداع البطني عند الأطفال؟
الصداع البطني عند الأطفال، حالة مُحيرة، غالبًا ما لا يُعرف سببها بوضوح. في حين أن الآليات الدقيقة لا تزال قيد البحث
أعراض الصداع البطني الرئيسية لدى الأطفال
Read more about صداع البطن عند الأطفال: الأعراض والإدارة
تحديد السبب الجذري: المفتاح للعلاج الفعال
اكتشف الدور الحيوي لتحليل السبب الجذري (RCA) في تحسين رعاية المرضى في بيئات الرعاية الصحية. توضح هذه الدليل الشامل أهمية RCA، حيث تعرض تقنيات فعالة مثل '5 لماذا' ومخططات العظام السمكية. تعرف على الفوائد العديدة لتنفيذ RCA لتحسين سلامة المرضى وتعزيز ثقافة التحسين المستمر داخل المنظمات الصحية. افهم التحديات التي تواجه RCA ولماذا تعتبر معالجة الأسباب الجذرية بدلاً من مجرد الأعراض أمرًا حاسمًا لتحقيق نتائج صحية على المدى الطويل. استكشف التطبيقات الواقعية، ودراسات الحالة في مختلف الصناعات، وأهمية التعاون بين المجالات في تحديد ومعالجة القضايا الصحية. قوى نفسك بالمعرفة لتحقيق صحة ورفاهية مستدامتين.
التحفيز المغناطيسي عبر الجمجمة (TMS) للصداع النصفي: ما هي الأدلة؟
التحفيز المغناطيسي عبر الجمجمة (TMS) للصداع النصفي: ما هي الأدلة؟
نصائح للسفر الجوي لتقليل عوامل تنشيط الصداع النصفي أثناء الرحلة
نصائح للسفر الجوي لتقليل عوامل تنشيط الصداع النصفي أثناء الرحلة
كيفية بناء شبكة اجتماعية داعمة عند المعاناة من الصداع النصفي
دليل شاملهل أنت أو أحد أحبائك تعاني من الصداع النصفي بشكل متكرر؟ فهم الأعراض المتنوعة المرتبطة بالصداع النصفي ضروري لفهم احتياجاتك الداعمة المحددة وإدارة الحالة.
المكملات الطبيعية للصداع النصفي: أيها يمتلك أقوى الأدلة؟
المكملات الطبيعية للصداع النصفي: أيها يمتلك أقوى الأدلة؟
فهم لاسمييديتان (ريفيو): كيف يختلف عن الأدوية الثلاثية
فهم لاسمييديتان (ريفيو): كيف يختلف عن الأدوية الثلاثية
مقارنة تطبيقات تتبع الصداع النصفي: الميزات والفوائد
مقارنة تطبيقات تتبع الصداع النصفي: الميزات والفوائد
ترجمة بحوث الصداع النصفي إلى استراتيجيات يومية عملية
ترجمة بحوث الصداع النصفي إلى استراتيجيات يومية عملية
كيفية التخلص من أدوية الصداع النصفي غير المستخدمة بأمان
كيفية التخلص من أدوية الصداع النصفي غير المستخدمة بأمان
حساسية الجلوتامات خارج مادة MSG: مصادر مخفية في الأطعمة
حساسية الجلوتامات خارج مادة MSG: مصادر مخفية في الأطعمة
