How NSAIDs Relieve Headache PainNSAIDs work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body that contribute to inflammation and pain. By reducing the levels of these prostaglandins, NSAIDs help to lessen the throbbing sensation and discomfort associated with headaches. This inhibition of prostaglandin production is a crucial aspect of their pain-relieving action.
Dosage and Administration: Important Considerations
The appropriate dosage of an NSAID for headache relief varies depending on the individual and the severity of the headache. It's essential to follow the instructions on the medication label carefully, or to consult a healthcare professional. Overuse or improper administration can lead to adverse effects. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns about the dosage.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While generally safe, NSAIDs can cause side effects, including stomach upset, nausea, and heartburn. Certain individuals may be more susceptible to adverse reactions, such as individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions. It's crucial to discuss any potential risks with a doctor before starting NSAID therapy, especially if you have a history of stomach problems or other health concerns.
Interactions with Other Medications
NSAIDs can interact with other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. For example, taking NSAIDs with blood thinners or certain diuretics can increase the risk of bleeding. It's essential to inform your doctor about all medications you're currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting an NSAID regimen. This detailed assessment helps avoid potentially harmful interactions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While NSAIDs are often effective for treating headaches, some headaches require immediate medical attention. If your headache is accompanied by fever, stiff neck, severe pain, or other concerning symptoms, such as visual disturbances or numbness, seek immediate medical help. Ignoring these warning signs could indicate a more serious underlying condition, and prompt medical intervention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The Crucial Role of GI Safety in NSAID Use
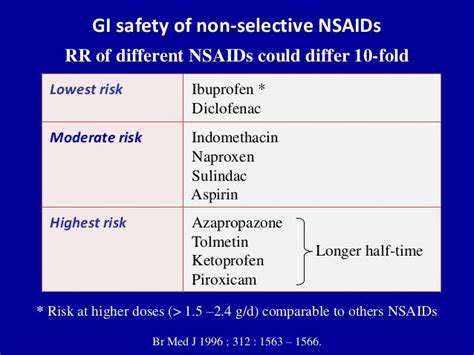
GI Safety Considerations in New Drug Development
Ensuring the safety of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract during the development of new drugs is paramount. Adverse GI effects can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and compliance with treatment regimens. Careful consideration of potential GI toxicity throughout the drug development process, from preclinical studies to clinical trials, is essential to minimize the risk of such effects. This involves rigorous testing to identify and characterize potential GI side effects and to develop strategies to mitigate them.
Early identification of potential GI safety issues is critical. Preclinical studies, using animal models, can provide valuable insights into the potential for GI toxicity associated with a new drug candidate. These studies can help identify the mechanisms of action and potential targets for GI side effects, providing crucial information for the design of subsequent clinical trials.
Clinical Trial Protocols and GI Monitoring
Clinical trials play a vital role in assessing the safety profile of new drugs, including their potential impact on the GI system. Rigorous clinical trial protocols must include specific assessments of GI adverse events. This involves collecting data on the frequency, severity, and type of GI symptoms reported by patients. This data collection must be standardized and comprehensive to ensure accurate and reliable assessment of the drug's safety.
Close monitoring of patients for GI symptoms throughout the clinical trial is critical. This includes regular assessments of symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and other relevant GI issues. These evaluations are crucial for identifying any emerging patterns or trends in GI adverse events and allow for timely intervention and adjustments to the trial protocol if necessary.
In addition to patient-reported outcomes, objective measures such as endoscopic examinations or blood tests may be incorporated into the monitoring process to provide a more comprehensive assessment of GI toxicity.
Strategies for Minimizing GI Toxicity
Once potential GI toxicity is identified, researchers must develop strategies to minimize or mitigate its impact. This may involve modifying the drug's formulation, dosage regimen, or administration route to reduce the exposure of the GI tract to the drug. These modifications aim to optimize the drug's absorption and minimize direct contact with sensitive GI tissues. Careful consideration of the drug's metabolism and excretion pathways is also necessary to predict and manage potential GI side effects.
Identifying alternative drug delivery systems can also be crucial. For instance, using enteric-coated formulations or developing drugs that are less irritating to the GI lining can help to reduce the incidence and severity of GI side effects. These strategies are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of new drugs while minimizing the impact on patients' lives.
Cardiovascular Risks Associated with NSAID Use
Gastrointestinal Issues
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), while effective for managing headaches, can significantly increase the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) problems. These range from mild discomfort like heartburn and indigestion to more serious conditions like ulcers and bleeding. Prolonged use or high doses of NSAIDs can irritate the stomach lining, potentially leading to inflammation, sores, and even perforations. It's crucial to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss them with your doctor, especially if you have a history of GI issues or are taking other medications that may interact with NSAIDs.
Kidney Problems
NSAIDs can also impact kidney function. In some individuals, they can reduce blood flow to the kidneys, potentially leading to acute kidney injury. This is particularly concerning for people with pre-existing kidney conditions or those taking other medications that can affect kidney function. It's essential to monitor kidney function closely if you're using NSAIDs regularly, especially for extended periods. Your doctor can help determine if monitoring is necessary for your specific situation.
Cardiovascular Events
A growing body of research suggests a potential link between NSAID use and an increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke. While the exact mechanism isn't fully understood, NSAIDs may influence blood pressure and blood clotting, increasing the risk of these adverse events. This risk is especially significant in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions or risk factors. It's essential to weigh the benefits of NSAIDs against these potential risks, especially if you have a family history of heart disease or are at risk for cardiovascular issues.
Interactions with Other Medications
NSAIDs can interact with a wide range of other medications, including blood thinners, diuretics, and some types of blood pressure medications. These interactions can significantly alter the effectiveness or safety of both the NSAID and the other medication. It's vital to discuss all medications you're taking with your doctor before starting NSAIDs, especially if you take multiple prescriptions. Your doctor can assess potential interactions and recommend appropriate adjustments or alternative pain management strategies.
Bleeding Risk
NSAIDs can inhibit the aggregation of platelets, which are essential for blood clotting. This can lead to an increased risk of bleeding, especially in individuals with pre-existing bleeding disorders or those taking other medications that affect blood clotting. This risk can manifest in various ways, from nosebleeds and easy bruising to more serious complications like gastrointestinal bleeding. It's critical to discuss the potential bleeding risk with your physician, especially if you have a history of bleeding disorders or are taking other medications that can increase the risk of bleeding.
High Blood Pressure
Some studies suggest a potential link between NSAID use and an increased risk of high blood pressure. NSAIDs can affect the body's regulation of blood pressure, leading to elevated readings in susceptible individuals. This risk is particularly important for people with pre-existing hypertension or risk factors for high blood pressure. Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential when using NSAIDs, especially for prolonged periods, to ensure blood pressure remains within a healthy range. Your doctor can advise on the best approach to manage blood pressure while using NSAIDs.
Importance of Individualized Approach
It's crucial to understand that the risks associated with NSAID use vary significantly depending on individual factors, including age, overall health, pre-existing conditions, and other medications being taken. A personalized approach to NSAID use is essential for headache relief. Consult your physician to discuss the potential benefits and risks of NSAID use for your specific needs and health status. Your doctor can help you determine the most appropriate dosage, duration of use, and potential alternatives if necessary.
Minimalist wooden side tables enhance aesthetic appeal in compact living spaces.
Dosage Considerations and Patient Factors
Patient Age and Kidney Function
Age is a crucial factor in determining NSAID dosage. Elderly patients, particularly those with pre-existing kidney conditions, are more susceptible to adverse effects from NSAIDs due to reduced kidney function. This reduced function can lead to slower drug elimination, resulting in higher drug concentrations in the body and a greater risk of complications like kidney damage. Therefore, careful monitoring and lower starting doses are often necessary in elderly patients and those with impaired kidney function. Appropriate adjustments to the dosage regimen should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional to manage the risk of adverse effects while still providing effective headache relief.
Kidney function tests (e.g., creatinine levels) are often used to assess the patient's ability to process NSAIDs, and this information is critical for determining the appropriate dosage to avoid potential kidney problems. Healthcare providers should consider the patient's baseline kidney function when prescribing NSAIDs, and adjustments should be made as needed based on ongoing monitoring of renal function.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Patients with pre-existing conditions like gastrointestinal ulcers, heart disease, or high blood pressure should exercise caution when using NSAIDs. These conditions can be exacerbated by NSAIDs, increasing the risk of complications. Understanding the patient's medical history is essential to determine whether NSAIDs are a suitable treatment option. A comprehensive discussion with a physician is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks of using NSAIDs for headache relief in these specific situations.
Certain medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders, can increase the risk of complications from NSAIDs, which can interfere with blood clotting. Therefore, patients with bleeding disorders require careful consideration before taking NSAIDs for headache relief. A doctor should be consulted to evaluate the patient's individual risk factors and determine if the benefits of NSAID treatment outweigh the potential risks.
Individual Tolerance and Response
Individual responses to NSAIDs can vary significantly. Some patients may experience minimal side effects at recommended dosages, while others may be more sensitive and experience adverse reactions. It's essential to monitor the patient's response to the medication closely. If a patient experiences any unusual symptoms or discomfort, they should report them to their healthcare provider immediately. Adjustments to the dosage or switching to a different NSAID may be necessary depending on the individual's tolerance and response.
Careful monitoring of the patient's condition during NSAID treatment is crucial. This includes noting any changes in symptoms, as well as any potential side effects, such as stomach upset, nausea, or dizziness. Adjusting the dosage or medication type based on the patient's individual response can optimize treatment effectiveness while minimizing potential complications.
Drug Interactions
NSAIDs can interact with other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. It's essential to inform the healthcare provider about all medications the patient is currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This information helps to identify potential drug interactions and adjust the NSAID dosage or treatment plan accordingly. Many common medications, such as blood thinners or diuretics, can interact with NSAIDs, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding or other complications.
Dosage Frequency and Duration
The frequency and duration of NSAID use should be carefully considered to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Using NSAIDs for extended periods or at higher frequencies can increase the risk of gastrointestinal problems and kidney damage. Healthcare providers should prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to alleviate headache symptoms. Adhering to the prescribed dosage regimen is crucial to achieving optimal results while minimizing the potential for harm.
Patients should be educated on the importance of following the prescribed dosage and frequency instructions. Taking NSAIDs more frequently than recommended or for longer than necessary can lead to significant health risks. Adherence to the prescribed regimen and reporting any unusual symptoms are essential aspects of safe and effective NSAID use for headache relief.
Alternatives and Preventive Strategies
Dietary Modifications
Maintaining a balanced diet can play a significant role in managing headache triggers and supporting overall digestive health. Reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine intake can often lessen the frequency and intensity of headaches. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients and promotes a healthier gut microbiome, which may contribute to reduced inflammation throughout the body. This can potentially decrease the likelihood of headaches, and also aid in the overall well-being of the digestive system. It's important to pay attention to individual sensitivities and identify foods that might be exacerbating your headaches.
Hydration is also crucial. Dehydration can trigger headaches, so maintaining adequate fluid intake throughout the day is essential. Carrying a water bottle and making conscious efforts to drink water regularly can significantly reduce the risk of headaches. Furthermore, a balanced diet rich in fiber can promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation, a known headache trigger.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress is a significant headache trigger for many people. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine can be invaluable in preventing headaches. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress levels and promote a sense of calm. Finding activities that promote relaxation, such as spending time in nature or engaging in hobbies, can also be beneficial.
Getting enough sleep is another crucial component of stress management. Adequate sleep allows the body to repair and recover, reducing stress hormones, and promoting overall well-being. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can significantly impact stress levels and improve headache prevention.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to headache frequency and severity. Identifying and addressing these factors can be a key part of a preventative strategy. Regular exercise, while beneficial for overall health, can sometimes exacerbate headaches in individuals who are not used to it. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercise can help minimize this risk. It's important to listen to your body and adjust your activity level as needed.
Regular sleep patterns are equally important. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, helps regulate the body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine and ensuring a dark, quiet, and comfortable sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of headaches.
Alternative Therapies
Various alternative therapies may offer additional avenues for headache prevention and management. Acupuncture, for example, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, and it can be beneficial in reducing pain and inflammation. Other therapies, such as massage therapy and biofeedback, can help relax muscles and manage stress, potentially reducing headache frequency.
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, can help manage stress and anxiety, both of which can contribute to headaches. These practices promote relaxation and focus, potentially reducing the overall stress response and improving headache prevention.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
While NSAIDs are frequently used to treat headaches, understanding their potential side effects and utilizing them responsibly is crucial. Careful consideration of dosage, frequency of use, and potential interactions with other medications or dietary supplements is essential. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your medication regimen.
Regular use of over-the-counter pain relievers can sometimes lead to rebound headaches. This means that the pain relievers, while initially providing relief, can actually trigger or worsen headaches over time. It's important to use these medications judiciously and to take breaks when possible to avoid this potential side effect.
Disclaimer: All articles on this site are original, please do not reprint
