Understanding the Initial Trigger
Pinpointing what initially sets off a headache plays a pivotal role in crafting successful prevention approaches. Triggers vary widely, ranging from dietary items like mature cheeses and cured meats to environmental elements such as potent odors or shifts in atmospheric pressure. Becoming aware of these catalysts enables individuals to take preventive measures, possibly decreasing how often and how severely headaches occur. Early recognition also aids in differentiating between headache types, as distinct triggers frequently correlate with particular headache profiles.
Environmental Factors as Headache Triggers
Surroundings can profoundly affect headache onset. Intense or flashing lights, jarring sounds, or powerful scents may all serve as catalysts. Variations in air pressure, commonly linked to weather changes, can similarly prompt headaches. Identifying which environmental aspects influence your headaches empowers you to shape a more regulated space. Solutions might include donning sunglasses in glaring light, employing noise-blocking earphones, or preparing for weather transitions.
Additionally, unstable temperatures and poor air quality can substantially contribute to headache initiation. Preserving consistent environmental conditions, both thermally and atmospherically, may help reduce headache probability.
Dietary Factors and Headache Triggers
Food selections can markedly sway headache occurrence and severity. Items like ripened cheeses, preserved meats, and cocoa are established triggers for numerous people. Insufficient hydration represents another critical nutritional consideration that's frequently neglected. Ensuring proper fluid intake through regular water consumption often proves transformative in warding off headaches.
Lifestyle Factors and Headache Prevalence
Daily habits significantly affect headache development and control. Sleep deficiency, anxiety, and improper body alignment all stand as notable contributors to headache frequency. Consistent physical activity and regulated sleep patterns can dramatically influence headache incidence. Anxiety-reduction methods, including controlled breathing or meditation practices, may also help mitigate stress-related headache triggers.
Stress and Its Impact on Headaches
Tension serves as a major factor in various health concerns, headaches included. Persistent stress can intensify existing headache tendencies and even initiate new ones. Acknowledging the relationship between stress and headaches permits the adoption of tension-reducing approaches. These might encompass relaxation methods, organizational skills, or obtaining expert assistance for managing prolonged stress.
Sleep Deprivation and Headache Connections
Sufficient rest is fundamental for general health, and sleep shortage can substantially affect headache patterns. Insufficient sleep may result in heightened tension headaches, migraines, and other headache varieties. Implementing regular sleep hours, developing calming pre-sleep rituals, and ensuring an optimal sleep setting all represent vital measures for lessening sleep deprivation's effect on headaches. Steady sleep routines can markedly enhance headache control.
The Role of Hormonal Factors and Lifestyle in Male Migraine
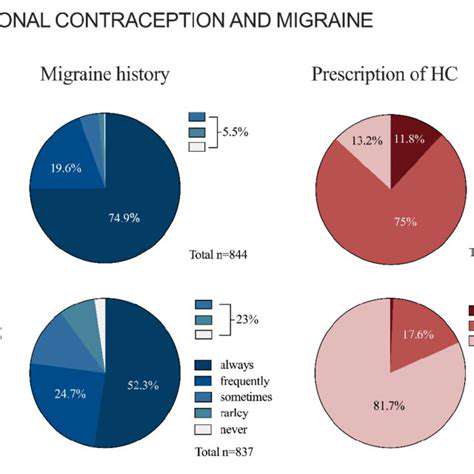
The Interplay of Hormones and Lipid Metabolism
Hormones serve critical functions in managing fat metabolism, affecting how fats are created, stored, and processed. They operate as biochemical communicators, synchronizing diverse bodily operations to preserve energy equilibrium. This sophisticated hormonal system guarantees the body maintains proper fat quantities for energy generation and cellular activities.
Various hormones produce distinct impacts on fat metabolism. For instance, insulin encourages fat storage as triglycerides in fat tissue, whereas glucagon prompts their release from storage areas. This precise equilibrium proves indispensable for sustaining healthy fat levels and avoiding metabolic irregularities.
The Impact of Insulin on Lipid Metabolism
Insulin, a vital pancreatic hormone, holds central importance in controlling sugar and fat metabolism. It instructs the body to assimilate blood sugar and stockpile it as glycogen in the liver and muscles. This mechanism directly affects fat metabolism by fostering triglyceride production in fat tissue, aiding energy conservation.
Moreover, insulin obstructs the disintegration of stored fats, preventing undue liberation of fatty acids into circulation. This synchronized action ensures efficient utilization of sugars and fats while hindering dangerous fat accumulation.
The Role of Glucagon in Lipid Mobilization
Glucagon, another pancreatic hormone, opposes insulin's effects by activating stored fat breakdown. It prompts fatty acid release from fat deposits, supplying an alternate energy reservoir when sugar levels diminish. This procedure proves crucial for preserving blood sugar concentrations during fasting or heightened energy requirements.
Exact control of glucagon secretion is imperative for preventing extreme fat mobilization and sustaining proper fat metabolism balance. This meticulous interaction between glucagon and insulin proves critical for averting metabolic disturbances.
The Influence of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones, encompassing thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are indispensable for governing multiple metabolic processes, including fat metabolism. These hormones affect fat burning and creation rates, impacting the body's capacity to process and store fats.
Increased thyroid hormone levels can accelerate fat breakdown and combustion, resulting in greater energy consumption. Conversely, decreased levels may decelerate these mechanisms, influencing fat metabolism and potentially causing fat profile changes.
The Effect of Growth Hormone on Lipid Metabolism
Growth hormone (GH), produced by the pituitary gland, fulfills a multifaceted role in fat metabolism. It encourages fatty acid liberation from fat tissue, offering an alternative energy source when necessary. This influence proves especially significant during growth phases and developmental stages.
Growth hormone also affects protein synthesis and other bodily components. This complex interaction of effects on fat and protein metabolism underscores growth hormone's diverse responsibilities in comprehensive metabolic operations. It's essential for appropriate growth and development, along with preserving metabolic stability.
The Significance of Cortisol in Lipid Metabolism
Cortisol, a stress hormone generated by adrenal glands, modifies fat metabolism in multiple manners. It activates fatty acid discharge from fat deposits, rendering them accessible for energy production. This reaction proves vital for coping with stress and maintaining blood sugar during high-demand periods.
However, prolonged stress and heightened cortisol concentrations can disrupt fat metabolism regulation, elevating metabolic disorder risks. This emphasizes the value of stress management and maintaining healthy cortisol levels for ideal fat metabolism and general wellbeing.