The Major Organ Systems of the Body
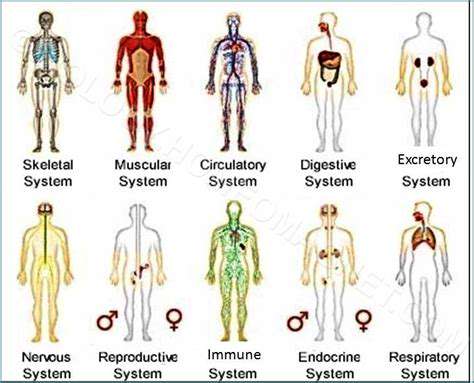
The Circulatory System
The circulatory system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health by transporting blood, nutrients, oxygen, and hormones throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, all working in harmony. This system ensures that every tissue receives the substances necessary for their function and vitality.
The heart acts as the pump of the circulatory system, contracting rhythmically to circulate blood. It is divided into four chambers: the right and left atria, and the right and left ventricles.
Blood vessels are categorized into three types: arteries, veins, and capillaries. Each type serves a specific function, with arteries carrying oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
In addition to blood flow, the circulatory system also plays a vital role in thermoregulation and the immune response, helping the body maintain a stable internal environment while responding to external changes.
The Digestive System
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and cell repair. It comprises various organs, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas.
Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is mechanically broken down by chewing and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that start the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates. From there, it travels down the esophagus to the stomach, where it is further mixed with gastric juices.
The stomach serves as a temporary storage site and site of enzymatic digestion, converting food into a semi-liquid substance called chyme. This chyme then moves to the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs.
Each component of the digestive system works cohesively to ensure that nutrients are efficiently extracted and waste materials are eliminated, maintaining the body’s overall health and function.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is an intricate network of neurons that transmits signals throughout the body, coordinating movement and sensory perception while regulating bodily functions. It is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord, serving as the control center for processing information and responding to stimuli. The brain interprets sensory data, while the spinal cord transmits messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The PNS includes all the nerves that branch out from the CNS, connecting it to the limbs and organs. It is further divided into the somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary movements, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate and digestion.
Overall, the nervous system is essential for maintaining homeostasis, allowing the body to respond swiftly to environmental changes and internal stimuli, ensuring optimal functioning of all other organ systems.
The Importance of Understanding Anatomy

Foundation for Healthcare Professions
Understanding human anatomy is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in healthcare. This knowledge provides medical professionals with the foundational skills required for diagnosis and treatment. A solid grasp of anatomy enhances the ability to communicate effectively with colleagues and patients alike.
Medical students, nurses, and physical therapists all rely on anatomical knowledge to understand patient needs. By knowing the correct terms and functions of body structures, they can administer treatments with precision.
Moreover, this foundational knowledge enables healthcare professionals to recognize abnormalities in body structure during examinations. This is particularly important in diagnosing conditions accurately and promptly, leading to better patient outcomes.
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of human anatomy fosters confidence in healthcare practitioners, allowing them to provide high-quality care. Being well-versed in the body's systems can significantly impact the effectiveness of treatments and interventions.
The Role of Anatomy in Education and Research
Anatomy plays a vital role not only in medical education but also in scientific research. It serves as a cornerstone that informs many fields, including biology and physiology. Without a solid understanding of anatomy, researchers would struggle to interpret their findings accurately.
For students, engaging with anatomical studies enhances critical thinking and analytical skills. Students often engage in hands-on activities such as dissections, which deepen their understanding of complex body structures.
Research in anatomy can lead to groundbreaking medical advancements, as it uncovers how structures function and interact with each other. This knowledge can drive innovations in surgical techniques, rehabilitation strategies, and medical technologies.
Furthermore, a comprehensive grasp of anatomy can contribute to public health initiatives. Understanding how anatomical knowledge applies to population health can aid in developing strategies for disease prevention and health promotion.