Common Severe Symptoms Associated with Head Pain
Understanding the Impact of Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are often associated with severe headaches, such as migraines or cluster headaches. These symptoms can compound the discomfort, making it difficult for individuals to find relief. They may also lead to dehydration if not managed properly. It's essential to identify when these symptoms arise alongside head pain, as they can indicate a more serious condition. Individuals experiencing this combination should consider seeking medical advice promptly.
In some cases, nausea can accompany neurological symptoms, signaling a need for immediate attention. Understanding the relationship between nausea/vomiting and head pain can be crucial for effective treatment. Treatment options may include medication to alleviate nausea, as well as pain management strategies. This dual approach can help improve the overall quality of life for those affected.
Documenting the frequency and severity of these symptoms can be beneficial for healthcare providers in diagnosing underlying issues. Keeping a headache journal that includes instances of nausea may aid in identifying triggers or patterns over time. By maintaining clear communication with healthcare professionals, patients can better manage their conditions.
Persistent nausea or vomiting with head pain should not be ignored. These symptoms could indicate conditions like meningitis or increased intracranial pressure, both of which require immediate medical assessment. Adhering to prescribed treatment plans becomes vital in managing such severe presentations effectively.
Consulting with a healthcare provider upon experiencing these symptoms can ensure proper diagnosis and treatment pathways are established. Early intervention can prevent the worsening of symptoms and improve outcomes for individuals experiencing severe head pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Severe Head Pain
Recognizing the right moments to seek medical attention for severe head pain is critical for health and safety. If someone experiences a sudden and intense headache, often described as a "thunderclap" headache, this requires immediate medical evaluation. This type of headache can signify serious medical conditions such as a brain aneurysm or stroke.
Additionally, if head pain is accompanied by neurological symptoms—such as confusion, weakness, speech difficulties, or vision changes—it is essential to seek urgent care. These signs may indicate a more severe underlying problem that could be life-threatening. Understanding these warning signs can empower individuals to act swiftly.
Headaches following a head injury should also prompt immediate medical assessment. Symptoms like dizziness, persistent vomiting, or loss of consciousness may suggest a concussion or other traumatic brain injury. Early intervention in these cases can significantly improve recovery outcomes and prevent further complications.
Furthermore, if severe headaches occur with significant changes in pattern, frequency, or intensity, medical advice should be sought. Changes in the nature of headaches might suggest new health issues or conditions requiring attention. It's essential always to listen to your body and act according to the signals it provides.
In conclusion, being aware of when to seek medical care for severe head pain can be a lifesaving decision. Keeping track of symptoms and being proactive in addressing them is vital in managing one’s health effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding When Symptoms Warrant a Doctor's Visit
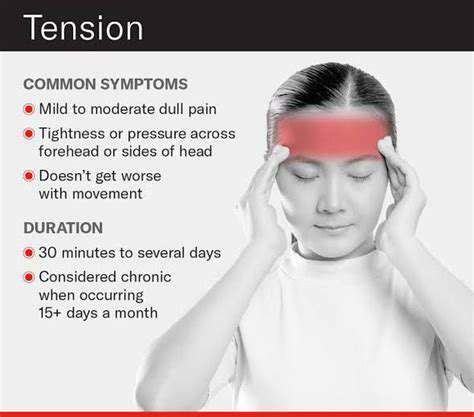
Head pain can be a common ailment, often resulting from tension, dehydration, or allergies. However, certain symptoms accompanying head pain can signal a more serious condition. Recognizing these signs is crucial for timely medical intervention.
One of the critical symptoms to consider is a sudden and severe headache, often described as a "thunderclap" headache. This type of pain may indicate an underlying issue such as a brain aneurysm or a hemorrhage, which necessitates immediate medical evaluation.
Other alarming features include confusion or difficulty speaking. If head pain is accompanied by symptoms affecting cognitive function, it may suggest a stroke or other neurological disorder. In such cases, treating the underlying cause quickly is vital to preventing long-term damage.
Similarly, if head pain occurs after a head injury, even if the pain is not immediately severe, it's important to consult a healthcare provider. The delayed onset of symptoms can indicate a concussion or other traumatic brain injury.
Additionally, if you experience visual disturbances, such as blurred or double vision, alongside head pain, this could suggest increased intracranial pressure or other serious eye health issues. Seeking medical attention promptly can help address these concerns effectively.
Other Warning Signs That Should Prompt Quick Action
In some cases, head pain may be accompanied by fever, stiffness in the neck, or rash. These symptoms can be indicative of meningitis or another infection affecting the central nervous system. Meningitis particularly requires urgent treatment to prevent severe complications.
Another red flag is unilateral weakness or numbness. If you or someone else experiences these symptoms in conjunction with head pain, it could be a sign of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke, which necessitates emergency care.
Persistent vomiting along with head pain is also a concerning sign. While occasional nausea can occur with headaches, continuous vomiting may indicate increased pressure in the skull or other serious medical conditions that require attention.
Additionally, bizarre behaviors or personality changes following head pain can signal underlying neurological issues. Such changes warrant a neurological evaluation to rule out serious concerns like tumors or encephalitis.
Being vigilant about these symptoms and understanding their implications can empower individuals to seek appropriate care when needed. When it comes to head pain complications, erring on the side of caution is always the safer choice.