What Causes Muscle Tension and Strain?
Understanding Muscle Anatomy and Function
The complexity of muscle anatomy plays a crucial role in how muscle tension and strain occur. Muscles are made up of fibers that work in synchrony to enable movement. When these fibers are stressed without adequate recovery, they may suffer from tension or strain.
Each muscle is innervated by nerves, and the communication between the muscle fibers and the nervous system is vital for maintaining proper tension. When this communication is interrupted, such as through injury or overuse, the balance needed for normal muscle function can be disrupted.
Ligaments and tendons also contribute significantly to muscle function, connecting muscles to bones and facilitating movement. Overstretching or tearing these connective tissues can lead to painful strain, affecting the surrounding muscles as well.
Moreover, understanding the types of muscle fibers—slow-twitch and fast-twitch—can help explain why certain activities cause more strain than others. Slow-twitch fibers are more resistant to fatigue, while fast-twitch fibers generate rapid force but are more prone to injury when not conditioned properly.
Common Causes of Muscle Tension
Muscle tension can arise from a multitude of factors, including physical exertion, poor posture, and stress. Engaging in repetitive motions without proper warm-up can lead to muscle overload, resulting in tension. Individuals in jobs that require them to sit for long durations often experience tension due to inadequate ergonomics.
Additionally, emotional stress can manifest as physical tension, leading to tightness in areas like the neck, shoulders, and back. Chronic stress may contribute to a cycle of muscle tension that can exacerbate overall discomfort and lead to fatigue.
Dehydration and poor nutrition are also significant contributors to muscle tension. Lacking essential nutrients such as potassium or electrolytes can impair muscle function and coordination, increasing the likelihood of strain during physical activities.
Finally, inadequate recovery after intense workouts often results in muscle fatigue and tension. Ignoring recovery needs can build up muscle tightness over time, disguising the initial symptoms that could have been addressed early on.
The Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices greatly influence muscle health and can either exacerbate or alleviate tension. For instance, those who maintain a sedentary lifestyle are often more prone to developing muscle tension due to inactivity. Muscles need regular movement to stay flexible and strong, so prolonged immobility is detrimental.
On the other hand, excessive vigorous exercise without proper conditioning or rest can also lead to muscle strain. It's vital that individuals find a balance in their physical activity levels to minimize the risk of injury.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can further complicate muscle health. Smoking restricts blood flow and oxygen circulation, which are crucial for muscle recovery, while excessive consumption of alcohol may lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies.
Incorporating a well-rounded diet and an active lifestyle that includes strength training, flexibility exercises, and aerobic activities can greatly reduce the likelihood of experiencing muscle tension and strain over time.
Recognizing Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Identifying the symptoms of muscle strain is essential for effective treatment and prevention. Initially, individuals may experience localized pain or discomfort when the affected muscle is used. This can manifest during activities or even at rest.
Additonally, swelling and bruising may occur around the strained muscle, as the body responds to the injury with inflammation. This reaction can hinder mobility and further contribute to a cycle of muscle tightness.
A general increase in muscle stiffness and reduced flexibility may indicate that a strain has occurred. If muscle strain is severe, individuals may be unable to use the affected muscle without significant pain, indicating a need for medical evaluation.
Ultimately, recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt interventions, potentially reducing recovery time and preventing further complications associated with muscle tension and strain.
Effective Treatments and Remedies for Muscle Strain
Treating muscle strain effectively often begins with the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This approach can help to alleviate immediate pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area. Rest is critical to allow the muscle time to heal without further strain.
Applying ice to the strained muscle can minimize swelling and numb pain, while compression wraps can provide additional support and reduce swelling. Elevation can help increase blood circulation and expedite the recovery process.
After the acute phase, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can facilitate recovery. Engaging in physical therapy under professional guidance may also be beneficial for more serious strains, allowing for structured rehabilitation.
In addition to these methods, over-the-counter pain relief medication may be used to manage discomfort during recovery. However, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any treatment regimen to ensure the highest quality of care.
Recognizing the Symptoms
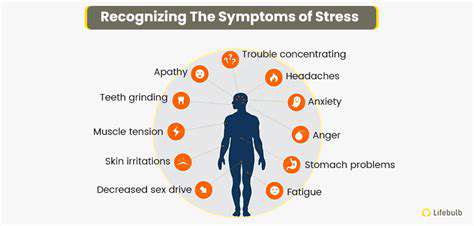
Common Symptoms of Muscle Tension
Muscle tension often manifests in various physical symptoms that can significantly affect daily life. Common signs include stiffness or tightness in one or more muscle groups, leading to discomfort and restricted movement. Individuals may also experience localized pain that can range from mild to intense, depending on the severity of the tension.
In addition to pain, many people report fatigue or a general sense of heaviness in the affected muscles. This fatigue can hinder one’s ability to perform everyday activities, creating a vicious cycle of pain and reduced mobility. It’s essential to recognize these signs early to address the underlying issues effectively.
Moreover, muscle tension can also induce secondary symptoms such as headaches or neck pain, which may not be directly related to the primary area of tension. These referred pains often complicate the situation, leading to further discomfort. Awareness of these symptoms can facilitate early intervention and prevent chronic conditions.
Physical Effects of Muscle Strain
Muscle strain can lead to various physical effects, including inflammation and swelling around the injured area. This inflammatory response is the body’s way of protecting the muscle, but it can restrict movement and add to overall discomfort. It is crucial to monitor these physical changes, as they can indicate whether the strain is worsening.
Additionally, strained muscles may exhibit reduced strength and endurance, making it challenging to maintain regular exercise routines. As strength diminishes, individuals may find themselves more susceptible to further injuries, creating a dangerous cycle of strain and tension. Understanding these consequences can encourage proactive care and rehabilitation to regain strength.
Furthermore, prolonged muscle strain without adequate rest can lead to chronic pain conditions, such as myofascial pain syndrome or fibromyalgia. These conditions can complicate treatment and recovery, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice if symptoms persist. Early recognition and intervention are key to preventing long-term issues.
Emotional and Psychological Impacts
The experience of muscle tension and strain is not purely physical; it can also have profound emotional and psychological effects. Individuals suffering from persistent muscle tension may experience increased stress, anxiety, or irritability, influencing their overall mental health. Understanding the connection between physical pain and emotional well-being is essential for holistic treatment.
Moreover, chronic pain can lead to feelings of helplessness or frustration as individuals struggle to engage in activities they previously enjoyed. This emotional toll often exacerbates the physical symptoms, creating a challenging cycle that can be difficult to break. Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of muscle strain is vital for comprehensive recovery.
Additionally, therapies that focus on mental well-being, such as mindfulness or cognitive-behavioral techniques, can complement physical treatments. Individuals can gain valuable tools to cope with pain and reduce stress, enhancing their overall quality of life. Recognizing and validating these emotional responses can greatly aid in the recovery process.
Prevention Strategies for Muscle Tension
Preventing muscle tension starts with awareness of proper body mechanics and posture, especially for people with sedentary lifestyles. Maintaining an ergonomic workspace and practicing good posture can significantly reduce the risk of strain. Simple adjustments can lead to impressive long-term benefits in muscle health.
Incorporating regular physical activity into one’s routine is another effective strategy to prevent muscle tension. Strengthening and stretching exercises can improve flexibility and reduce the likelihood of injury during routine activities. Additionally, engaging in low-impact activities like yoga can promote relaxation and help to alleviate existing tension.
Lastly, managing stress effectively through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can be highly beneficial. These methods not only help in reducing physical symptoms but also enhance overall mental resilience. Adopting a proactive approach to stress management can create a significant impact on muscle health.
Treatment Options for Muscle Strain
When muscle tension or strain occurs, various treatment options are available to promote healing and alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may provide immediate relief and reduce inflammation. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Physical therapy is often recommended for those suffering from persistent muscle strain, focusing on personalized exercises designed to strengthen and reduce tension in the affected areas. Therapy may also include modalities like heat, massage, or ultrasound to facilitate recovery. Engaging with a qualified therapist can greatly enhance the effectiveness of the rehabilitation process.
In some cases, more advanced treatments like corticosteroid injections or even surgical options may be necessary if conservative treatments fail. However, these options are typically reserved for severe cases. A comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, exercise, and medical intervention can optimize recovery and prevent recurrence.
Preventative Measures to Avoid Muscle Tension and Strain
Understanding the Importance of Proper Warm-Up Techniques
Beginning any physical activity or workout session without proper warm-up can set the stage for muscle strain. A well-structured warm-up routine increases blood flow to your muscles, preparing them for the exertion ahead. It not only enhances performance but also significantly reduces the risk of injuries such as sprains and strains. Incorporating dynamic stretches like leg swings and arm circles can prime your muscles and joints effectively.
In addition to physical readiness, a proper warm-up aids in improving flexibility, which is crucial in preventing muscle tension. When the body is well-prepared, the likelihood of sustaining injuries during intense activity drops considerably. Engaging in a warm-up session does not have to be time-consuming; even 10 to 15 minutes can yield substantial benefits if executed correctly, ensuring a seamless transition into your main workout.
Moreover, warming up is not only about the body. It's important to prepare mentally as well. A warm-up provides you the opportunity to focus your mind on the activity ahead, setting a tone of discipline and commitment. A clear mental state, combined with physical readiness, enables a complete approach to injury prevention, creating a holistic understanding of bodily movements during physical exertion.
Incorporating Strength Training and Flexibility Exercises
Integrating strength training into your fitness regimen can significantly boost muscle resilience and overall stability. Strong muscles are more capable of handling stress and strain, thus reducing the risk of injuries. Regularly practicing resistance exercises targeting all the major muscle groups helps in building a sound foundation that supports all physical activities. Furthermore, incorporating core-strengthening exercises is vital as they play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture and alignment.
Flexibility exercises, such as yoga and Pilates, should also be part of a comprehensive fitness strategy. These practices not only enhance range of motion but also release muscle tension built up from repetitive or intense activity. Stretching muscles regularly aids in keeping them elongated, preventing stiffness, and fostering a balanced approach to strength and flexibility. Ideally, a combination of these modalities ensures an all-around development of physical fitness.
Establishing a routine that emphasizes both strength and flexibility can help promote muscle health while effectively mitigating tightness and pain. It is essential, however, to tailor these programs according to individual needs, taking into account your specific activity levels, age, and physical conditions. Consulting with a fitness professional can help customize a plan that addresses your unique requirements and goals, further enhancing your muscle wellness.
Treatment Options for Muscle Tension and Strain
Understanding Muscle Tension: Causes and Symptoms
Muscle tension can stem from various causes, including physical exertion, emotional stress, and poor posture. This chronic tightness may lead to discomfort, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Individuals often report that specific activities exacerbate the tension, making it essential to understand the underlying factors contributing to the issue. Identifying these causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention strategies.
Symptoms of muscle tension often include localized discomfort or pain and may also present as headaches or fatigue. Some individuals may experience restricted movement, making it challenging to perform daily tasks. Recognizing these symptoms early can facilitate timely intervention, potentially preventing further complications. Increased awareness of muscle tension can help individuals take proactive measures.
Stress and anxiety are significant contributors to muscle tension, with many people unconsciously tensing their muscles in response to mental strain. It's important to address these emotional factors alongside physical treatment options. Regular self-assessment of mental well-being can lead to better management of muscle-related issues. Stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and meditation, can play a key role in alleviating symptoms.
Additionally, athletes and those involved in physical activities are at greater risk of developing muscle tension due to repetitive movements and intense exertion. Understanding the nature of these activities can help develop specific preventive measures. For example, warm-ups and cool-downs can be integral in minimizing the risk of muscle strain, contributing to overall performance and well-being.
A thorough examination by healthcare professionals can reveal the full scope of muscle tension issues. Identifying specific muscle groups that are affected can lead to targeted treatment plans. Whether through physical therapy, chiropractic care, or medical intervention, understanding the causes and symptoms of muscle tension is the first step towards effective management.
Non-Invasive Treatment Options
Non-invasive treatment options for muscle tension and strain are often the first line of defense for those experiencing discomfort. These methods primarily include physical therapy, stretching exercises, and hot or cold therapy. Physical therapy focuses on alleviating pain through targeted exercises designed to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Patients work closely with therapists to develop personalized regimens that address their unique needs.
Stretching exercises can be remarkably effective in relieving muscle tension and promoting relaxation. Incorporating a variety of stretches into your daily routine can enhance flexibility and blood circulation to tense areas. Simple stretches can be performed at home or integrated into a warm-up routine before physical activities, ensuring that muscles are prepared for exertion. The importance of consistency in practice cannot be overstated, as regular stretching can lead to lasting benefits.
Hot and cold therapy can also provide significant relief from muscle tension. Heat can help relax and loosen tissues, promoting increased blood flow to the affected area. Conversely, cold therapy helps reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. Alternating between hot and cold treatments may offer the most comprehensive relief; however, individuals should always listen to their bodies and apply therapies according to personal comfort and sensitivity.
Yoga and acupuncture are additional non-invasive options that have gained popularity for their holistic approaches to treating muscle tension. Yoga emphasizes relaxation, balance, and proper alignment, which can significantly reduce muscle tightness over time. Acupuncture, on the other hand, targets specific points along the body's meridians, promoting energy flow and alleviating tension. Both practices work best in conjunction with other treatments, creating a well-rounded approach to muscle health.
Lastly, lifestyle modifications, such as ergonomic workplace adjustments and mindfulness practices, are essential for managing muscle tension proactively. Small changes can yield considerable benefits, leading to more significant improvements over time. When combined with non-invasive treatments, these strategies can enhance one's overall quality of life and maintain ongoing muscle health effectively.
Medications and Alternative Therapies
For cases of muscle tension and strain that do not respond to non-invasive treatments, medication can play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms. Common over-the-counter options include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen. These medications can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, enabling individuals to engage in physical activities with less discomfort. Consultation with a healthcare provider is vital to determine the most appropriate medication for each situation.
In certain cases, muscle relaxants and prescription medications may be necessary. These medications work by inhibiting nerve signals to the muscles, leading to decreased spasms and greater relaxation. While they can be effective in managing severe tension, these treatments should be pursued under professional supervision due to the potential for side effects and dependency. A comprehensive approach that includes medication and other therapies is often recommended.
Alternative therapies are increasingly recognized for their potential benefits in treating muscle tension. For example, massage therapy can relieve muscle tightness by promoting blood circulation and facilitating relaxation. A skilled massage therapist can target specific muscle groups to decrease tension effectively. Some individuals may explore different modalities such as deep tissue massage, trigger point therapy, or myofascial release to find the best-fit approach.
Aromatherapy, which utilizes essential oils derived from plants, has gained traction for its soothing properties. Certain oils, like eucalyptus and lavender, are believed to promote relaxation and reduce tension when inhaled or applied during a massage. While scientific research on aromatherapy is ongoing, many people report positive effects on their overall well-being. Integrating aromatherapy with traditional treatments can enhance the overall therapeutic experience.
Finally, integrating holistic practices such as chiropractic care or naturopathy may provide additional avenues for addressing muscle tension. Chiropractors utilize spinal adjustments and manipulations to optimize body alignment, subsequently promoting better function and reducing muscle strain. Naturopathy, which emphasizes natural and preventative care, may suggest lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and herbal remedies that cater to individual health challenges, including muscle tension. Combining these approaches can lead to a synergistic effect, providing comprehensive support for muscle health.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing muscle tension and strain involves a proactive approach that includes both lifestyle changes and regular physical activity. Incorporating consistent exercise into daily routines strengthens muscles and improves endurance, which can significantly reduce the chances of developing tension-related conditions. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be ideal for building a solid foundation while minimizing wear and tear on the body.
Furthermore, adopting proper ergonomics in various environments plays a pivotal role in preventing muscle strain. This includes ensuring that workstations are set up to minimize strain on the neck, shoulders, and back. Regular breaks during prolonged sitting or repetitive tasks allow muscles to relax and recover, ultimately contributing to long-term health. Simple adjustments, such as using a chair with lumbar support, can yield considerable benefits.
Balancing a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can also support muscle health. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins promotes overall wellness. Foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help alleviate tension. Staying hydrated is equally crucial, as dehydration often exacerbates muscle tightness and cramps.
Stress management techniques can serve as vital tools in preventing muscle tension. Mindfulness practices like meditation, breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation cultivate awareness and promote relaxation. Regularly engaging in activities that foster mental well-being enhances emotional resilience, subsequently reducing the risk of stress-induced muscle tension. These techniques, combined with physical practices, create a balanced approach to health.
Lastly, maintaining a strong support system and nurturing relationships contribute to mental and emotional health. Engaging with family and friends, participating in social activities, or seeking professional support when needed creates a sense of community. This sense of belonging fosters resilience and coping skills, essential elements in managing everyday stressors that may contribute to muscle tension. Overall, a comprehensive prevention strategy can enhance well-being and lead to a healthier lifestyle.