Common Viral Infections
Understanding Viral Pharyngitis
Viral pharyngitis is one of the most prevalent causes of throat pain and inflammation. It is often characterized by symptoms such as a scratchy throat and difficulty swallowing. A thorough understanding of viral infections can help in managing symptoms effectively.
Common viruses that lead to pharyngitis include the common cold and influenza. Other viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus, can also be responsible for more severe throat pain. In most cases, the symptoms are self-limiting and will resolve without specific treatment.
It's important to differentiate between viral and bacterial infections to ensure appropriate treatment. Individuals experiencing severe throat pain or symptoms lasting more than a week should consult a healthcare provider.
Impact of Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergies can significantly contribute to throat pain, especially during certain times of the year. Allergens like pollen and mold can provoke inflammation and irritation in the throat. Additionally, post-nasal drip from allergies often leads to discomfort and soreness.
Those with known allergies are advised to manage their symptoms with antihistamines or other allergy relief medications. Staying hydrated and using humidifiers can also provide relief from throat irritation caused by dry air.
Recognizing the signs of allergic reactions is crucial for effective management. If throat pain persists despite controlling allergy symptoms, an evaluation for other underlying causes may be necessary.
Effects of Colds and Upper Respiratory Infections
Colds, caused by various viruses, often lead to throat pain as part of a broader array of symptoms. Alongside throat discomfort, individuals may experience nasal congestion, cough, and body aches. Throat pain from a cold typically arises from inflammation due to the viral infection.
Although colds are usually mild and resolve within a week, they can still significantly affect daily activities. Over-the-counter medications may help alleviate throat pain and other cold symptoms.
Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, is essential to prevent the spread of these viruses. Those experiencing severe symptoms, or symptoms that drastically worsen over a few days, should seek medical advice to rule out more serious conditions.
Bacterial Infections: Strep Throat
Bacterial Infections: Overview and Symptoms
Bacterial infections are a major cause of throat pain, with one of the most common being strep throat. This infection is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, a type of bacteria that can lead to severe inflammation in the throat. Individuals with strep throat often experience a sudden onset of symptoms that can be quite debilitating.
Common symptoms of strep throat include a severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes. The throat may appear red and swollen, with possible white patches or streaks that are indicative of pus. Some patients may also experience fever, headache, and body aches, which can exacerbate the discomfort associated with the infection.
It's important to note that strep throat is highly contagious and can spread rapidly, particularly among children and in close-contact environments such as schools. As such, early identification and treatment are crucial to managing symptoms and preventing further transmission.
If you suspect you have strep throat, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare provider can conduct a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm the infection and prescribe appropriate antibiotics to help alleviate symptoms and speed recovery.
Treatment Options for Bacterial Infections
Treatment for strep throat generally involves the use of antibiotics, which are effective in eliminating the bacteria responsible for the infection. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include penicillin and amoxicillin, which are typically administered for a duration of ten days. It is crucial for patients to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to help manage pain and reduce fever. Hydration is also vital as it helps soothe the throat and prevent dehydration, especially for individuals experiencing difficulty swallowing.
Resting the voice and avoiding irritants such as smoke or strong aromas can further support recovery. Gargling with warm salt water may also provide temporary relief for sore throat symptoms, as it can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
In some cases, if left untreated, strep throat can lead to more severe complications, such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation. Therefore, it is imperative to address symptoms of bacterial throat infections promptly and follow through with prescribed treatments.
Allergies and Environmental Irritants
Understanding Allergies and Their Impact on Throat Health
Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to substances that are typically harmless, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. This response can lead to inflammation in the throat, resulting in pain or discomfort. When these allergens are inhaled, they can irritate the mucous membranes, causing the throat to become scratchy and inflamed.
Common symptoms associated with allergy-induced throat pain often include a runny nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes. These symptoms can compound the discomfort, making it difficult for individuals to swallow or speak. Recognizing the connection between your environment and throat health can be the first step toward effective management and relief.
To mitigate throat pain caused by allergies, individuals may benefit from allergen avoidance strategies. Keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons, using air purifiers, and maintaining a clean home environment can significantly reduce exposure to triggers and alleviate symptoms.
Identifying Environmental Irritants
Environmental irritants such as smoke, pollution, and chemical fumes can significantly contribute to throat pain. These substances can cause direct irritation, leading to inflammation and soreness. Smoke from cigarettes or industrial environments can be especially detrimental, as it not only irritates the throat but can also exacerbate underlying conditions such as asthma.
Additionally, prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals commonly found in cleaning products can lead to throat discomfort. Symptoms often worsen in poorly ventilated areas where irritants can accumulate. Awareness of these irritants is important for maintaining throat health and overall well-being.
To counteract the effects of environmental irritants, individuals should aim to reduce their exposure. This might include avoiding smoking, using natural cleaning products, or wearing masks in polluted environments. Simple lifestyle changes can result in significant improvements in throat comfort.
The Role of Humidity and Temperature
Humidity levels and temperature can also play a critical role in throat health. Dry air, especially during winter months, can lead to throat irritation and discomfort. While temperature can vary widely, it's the dryness that often exacerbates symptoms, making the throat feel scratchy or raw.
Conversely, excessively humid conditions can encourage the growth of mold and dust mites, both of which can trigger allergic reactions and throat pain. It's essential to find a balance in your indoor environment to ensure optimal humidity levels, ideally between 30% and 50%.
Using humidifiers during dry seasons and ensuring proper ventilation can help maintain comfortable humidity levels. Regularly monitoring indoor climate conditions can significantly improve throat health and reduce instances of pain.
Prevention and Treatment Options
Preventing throat pain associated with allergies and irritants involves both avoiding triggers and implementing effective treatment strategies. For individuals with known allergies, over-the-counter antihistamines may help to alleviate symptoms. Consulting with an allergist can provide tailored management strategies.
In cases where environmental irritants are unavoidable, regularly using saline nasal sprays can help cleanse the nasal passages, reducing the impact on the throat. Drinking plenty of fluids and using throat lozenges can also provide temporary relief by soothing the irritated tissue.
For persistent throat pain, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include prescription medications or referral to an otolaryngologist for further evaluation. Being proactive in managing throat health can lead to better quality of life.
Acid Reflux and GERD
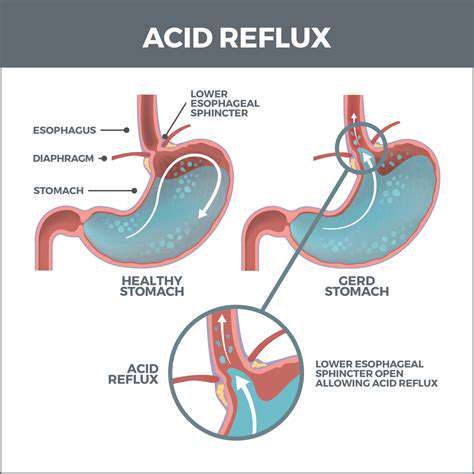
Understanding Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This backflow can lead to symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation. One significant trigger for acid reflux is the relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Factors such as obesity, pregnancy, and certain foods can contribute to this condition. Long-term untreated acid reflux can lead to more severe complications, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
The sensation of a bitter taste in the mouth often accompanies this condition. This occurs when stomach contents rise high enough to reach the throat. Persistent throat pain may indicate a more serious issue, such as esophagitis or Barrett's esophagus. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist over time. Early intervention can help in managing discomfort and preventing long-lasting damage.
Several lifestyle changes can help reduce acid reflux symptoms. Eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and not lying down soon after eating are effective strategies. Maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking can greatly improve overall esophageal health. Regular exercise, while avoiding high-impact activities after meals, is also beneficial. These modifications can lead to significant symptom relief.
Over-the-counter medications, such as antacids or proton pump inhibitors, can provide quick relief for occasional acid reflux. However, chronic symptoms might require a prescription plan. In some cases, if lifestyle modifications and medications fail, surgical options may be considered. Understanding your body’s responses is essential in effectively managing these symptoms. Keep a symptom diary to help identify triggers and patterns.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is characterized by frequent acid reflux occurrences. Common symptoms include persistent heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. In more severe cases, GERD may manifest as throat soreness or laryngitis. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment, improving quality of life. Many individuals are undiagnosed, attributing their discomfort to other causes.
A healthcare provider often diagnoses GERD through a combination of medical history and physical examination. Diagnostic tests such as an upper endoscopy or 24-hour pH monitoring can provide further insights. These tests help evaluate the severity of the condition and assess any potential damage to the esophagus. Based on these findings, your healthcare provider can formulate an effective treatment plan tailored to your needs.
In addition to traditional treatment methods, alternative therapies may assist in managing GERD symptoms. Natural remedies, dietary supplements, and relaxation techniques have shown positive results for some individuals. However, it is essential to consult with a professional before trying alternative approaches. Each person's response to treatments can vary greatly, so a customized approach is often necessary.
Monitoring lifestyle choices plays a pivotal role in managing GERD effectively. Keeping a food diary to track meals and symptoms can help identify problematic foods. Ensuring adequate fluid intake and incorporating more alkaline foods may also alleviate symptoms. Maintaining upright posture after meals and avoiding eating close to bedtime is recommended as well. Awareness of these aspects helps control and minimize the impact of GERD on daily life.
Other Causes of Throat Pain
Infections Leading to Throat Pain
Throat pain is often associated with infections such as viral or bacterial illnesses. Viral infections like the common cold and influenza can cause significant throat discomfort. These infections typically present with accompanying symptoms such as cough, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
Bacterial infections, most notably strep throat, can also be a significant cause of throat pain. Strep throat is caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, and it often requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications. Symptoms include severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and the presence of white patches on the tonsils.
In addition to these, other infections like mononucleosis can lead to throat pain. This condition is commonly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and is often accompanied by extreme fatigue and swollen lymph nodes.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Throat Pain
Environmental irritants play a crucial role in causing throat pain as well. Exposure to smoke, pollution, or harsh chemicals can irritate the throat lining, leading to discomfort and inflammation.
Allergies to pollen, dust, or pet dander can also trigger throat pain due to postnasal drip, which irritates the throat as mucus accumulates. Chronic sinus issues often exacerbate this problem, leading to persistent soreness.
Dry air, particularly in winter months, can cause throat pain by drying out the mucous membranes. Increasing humidity levels in your home can help alleviate this discomfort and promote throat health.