What is Muscle Tension?
Understanding the Causes of Muscle Tension
Muscle tension can arise from various sources, both physical and emotional. Physical factors may include repetitive movements, poor posture, and injuries. When muscles are overworked or used improperly, they can become tight and sore.
Emotional stress is another significant contributor to muscle tension. When individuals experience anxiety or stress, it can lead to the tightening of muscles, especially in the neck, shoulders, and back. This reaction is often linked to the body’s fight-or-flight response.
Dehydration and nutritional deficiencies can also play a role in muscle tension. A lack of essential nutrients and fluids can lead to muscle cramps and tightness, hindering overall physical performance and health.
Another common cause of muscle tension is insufficient rest and recovery. Engaging in strenuous physical activities without allowing adequate time for recovery can lead to prolonged muscle tension and discomfort.
Finally, medical conditions such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome can contribute to muscle tension. Understanding the underlying causes of muscle tension is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
Strategies for Managing Muscle Tension
One of the most effective ways to manage muscle tension is through regular stretching exercises. Stretching helps to elongate tight muscles, improve flexibility, and promote relaxation. Incorporating a routine of dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching afterward can significantly alleviate tension.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga, can also help in reducing muscle tension. These practices stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and can counter the effects of stress on the body.
Staying hydrated is crucial for muscle health. Drinking plenty of water can help to prevent muscle cramps and maintain optimal muscle function. Additionally, a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of electrolytes, vitamins, and minerals is important for muscle recovery and tension reduction.
Massage therapy is another effective way to relieve muscle tension. Regular massages can enhance blood circulation, reduce stiffness, and promote relaxation of the muscles. It is especially beneficial for individuals with chronic muscle tension or those recovering from injuries.
Lastly, ensuring proper ergonomics in daily activities, such as working at a desk or lifting objects, can prevent muscle strain and tension from developing. Investing time and effort in these strategies can lead to significant improvements in physical health and overall well-being.
Understanding Muscle Strain

What is Muscle Strain?
Muscle strain occurs when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn, often resulting from physical activity or overexertion. Understanding the symptoms of muscle strain is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common signs include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility in the affected area.
Muscle strains can vary in severity, categorized into three grades: Grade I (mild), Grade II (moderate), and Grade III (severe). The initial response to a muscle strain can drastically influence recovery time. Mild strains generally heal within a few weeks, while severe strains may require longer recovery or even surgical intervention.
A variety of factors can contribute to muscle strains, including inadequate warm-up, muscle imbalances, and poor conditioning. Awareness of one's physical limits and body mechanics can help in preventing these injuries from occurring.
Preventing Muscle Tension and Strains
Preventing muscle tension and strains involves a combination of proper conditioning, stretching, and warm-up exercises. Incorporating flexibility and strength training into your routine can significantly reduce the risk of injuries. Moreover, listening to your body signals and avoiding pushing beyond limits is essential.
Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet also play vital roles in muscle health. Nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals are key for muscle recovery and strength. Prioritizing good nutrition can fortify your muscles and improve overall physical performance.
Lastly, using proper techniques during physical activities and sports is fundamental. Whether lifting weights or engaging in sports, ensuring correct posture and movements minimizes the risk of strain and injuries.
Causes of Muscle Tension and Strain
Physical Activity and Overexertion
One of the most common causes of muscle tension and strain is excessive physical activity. When individuals push their bodies beyond normal limits—whether through sports, lifting heavy weights, or engaging in strenuous exercises—they can inadvertently put stress on their muscles. This overexertion can lead to soreness, tension, and even acute injuries that require time to heal.
Additionally, improper technique during physical activities can contribute to muscle strain. Without adequate training or awareness of body mechanics, people may perform exercises incorrectly, further increasing their risk of strain and tension. Ensuring proper form and gradually increasing workout intensity can help mitigate these risks.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Emotional stress is another significant contributor to muscle tension. When individuals are stressed, their bodies tend to respond with increased muscle tightness, especially in areas like the neck, shoulders, and back. This muscle tightness can become chronic, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility over time.
Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga, can help reduce muscle tension associated with psychological stress. By learning to relax both the mind and body, individuals can alleviate tension and promote better overall physical health.
Posture and Ergonomics
Poor posture, particularly in a sedentary lifestyle characterized by long hours of sitting, can lead to significant muscle strain. Slouching at a desk, cradling a phone between shoulder and ear, or improper seating arrangements can place undue stress on specific muscle groups. These habits often lead to chronic pain and discomfort.
To counteract posture-related issues, it is crucial to cultivate awareness of body alignment and ergonomics. Regular breaks, stretching, and the use of ergonomic furniture can help maintain proper posture, thus reducing the likelihood of muscle tension and strain.
Inadequate Warm-up and Cool-down Practices
Another common factor contributing to muscle tension and strain is the neglect of proper warm-up and cool-down routines. Failing to adequately prepare the muscles for activity can lead to injuries, as cold or tight muscles are more susceptible to strains. Warm-up exercises increase blood flow and flexibility, preparing the body for more strenuous movements.
Similarly, cooling down post-activity helps prevent muscle stiffness. Stretching and allowing the heart rate to gradually decrease are essential elements that facilitate recovery and minimize muscle tension. Incorporating these practices into a fitness routine can enhance physical health and reduce injuries.
Preventing Muscle Tension and Strain
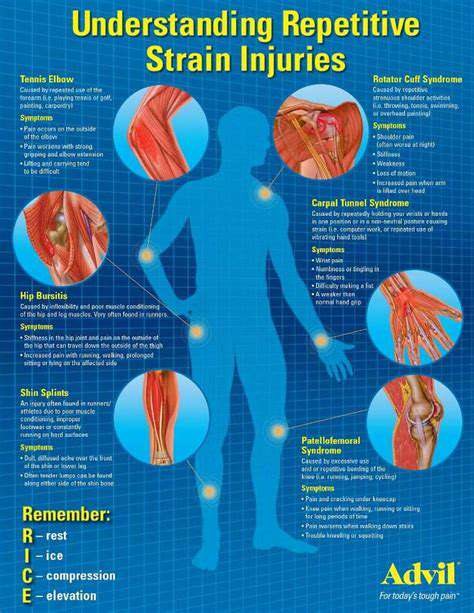
Understanding Muscle Tension
Muscle tension is the result of muscles contracting and not fully relaxing. This can lead to discomfort and pain if not managed properly. Recognizing the early signs of muscle tension is crucial for prevention. Factors such as stress, poor posture, and repetitive movements significantly contribute to muscle tension.
It is essential to understand that muscle tension can be both physical and psychological. Emotional stress often manifests as physical tension in the body. This connection underscores the importance of a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Different muscle groups may react uniquely to tension based on their usage and individual characteristics. For instance, the neck and shoulders are commonly affected by stress and poor ergonomics. Hence, awareness of high-tension areas can facilitate more targeted prevention strategies.
Ultimately, knowledge of how muscle tension develops informs better management and care practices. Regular self-assessment can help individuals gauge their body’s response to daily activities.
Effective Stretching Techniques
Stretching is one of the best ways to alleviate muscle tension and promote flexibility. Incorporating a routine of regular stretching can significantly enhance your muscle health. Dynamic stretches before activities warm up the muscles, while static stretches afterward help in recovery.
There are various techniques for stretching, such as static, dynamic, and PNF (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation). Each method has its benefits, depending on the goals set for muscle health. Understanding how to properly perform these techniques can prevent injury and enhance effectiveness.
When stretching, it’s important to maintain proper form to avoid overstretching. Hold each stretch for at least 15-30 seconds for optimal effect, and be mindful of your body’s signals. Never push through pain, as this can lead to injury rather than relief.
Incorporating breathing exercises with stretching can also enhance relaxation and muscle recovery. Deep, controlled breathing can help release tension in the muscles and prevent cramping.
Utilizing Proper Body Mechanics
Body mechanics involve using the body efficiently during physical activities. Understanding proper body mechanics can significantly reduce the risk of muscle strain. Using your body correctly can prevent unnecessary tension and promote overall physical health.
This involves maintaining a straight posture, proper lifting techniques, and ergonomic setups at work and home. For example, when lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees rather than the waist to protect your back. This principle applies to many everyday activities.
Incorporating proper body mechanics into daily activities helps to build awareness and create healthier habits. This proactive approach may require adjustments in how tasks are performed, but the long-term benefits are worth it.
Frequent reassessment of body mechanics during activities can also help identify areas for improvement. Educational resources, such as workshops or classes, can provide valuable knowledge on this topic.
Role of Exercise in Managing Tension
Regular exercise is a crucial component in managing muscle tension and strain. Engaging in physical activities helps to reduce stress while improving overall muscle function. Emphasizing both aerobic and strength-building exercises provides a comprehensive approach to muscle health.
Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, are particularly effective in reducing muscle tension. They promote relaxation and cardiovascular health, creating a balanced routine. Strength training, on the other hand, builds muscle resilience and reduces the risk of strain.
Consistency is key; integrating physical activity into your daily routine establishes healthier habits. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to maximize benefits. This can include short, frequent sessions or longer, less frequent workouts that fit your lifestyle.
Additionally, addressing muscle tension through exercise may also require targeted physical therapy or specialized training. Consulting a fitness or health professional can ensure that you are engaging in the most beneficial exercises for your specific needs.
Importance of Recovery and Rest
Recovery time is critical when managing muscle tension and strain. When muscles recover properly, they repair and become stronger. An essential aspect of recovery includes rest days and adequate sleep; both are vital for muscle health.
Active recovery techniques, such as light stretching or low-impact activities, can help soothe tense muscles. These actions promote blood flow and assist in the muscle recovery process. In contrast, prolonged inactivity can lead to stiffness and further tension.
Listening to your body is key when it comes to recovery. If you experience persistent pain or discomfort, it may signal the need for additional rest or professional assessment. Ignoring these signals can lead to more significant issues down the line.
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques can also enhance the recovery process. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, or tai chi can significantly reduce stress and promote muscle relaxation.
Managing Existing Muscle Tension and Strain
Understanding Muscle Strain and Its Causes
Muscle strain occurs when muscle fibers are stretched or torn, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Common causes of muscle strain include overuse, excessive force, and poor body mechanics during physical activities.
Factors such as dehydration, fatigue, and muscle imbalances can exacerbate the risk of strains. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for both prevention and effective management.
Common activities that lead to muscle strain include sports, heavy lifting, or even improper stretching. Being mindful of the body's limitations during these activities can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Recognizing the symptoms of muscle strain early, such as soreness or stiffness, can lead to quicker interventions and better outcomes.
Effective Techniques for Managing Muscle Tension
Managing muscle tension involves a combination of relaxation techniques, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation can help alleviate stress and reduce tension.
Incorporating regular stretching into your routine can improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness. Dynamic stretching before activities and static stretching after can be particularly beneficial.
Strengthening exercises for core muscles also play a vital role in maintaining overall muscle balance and function, helping to mitigate tension issues over time.
Lastly, practices such as yoga and Pilates can enhance body awareness and increase relaxation, making them effective tools for reducing muscle tension.
Utilizing Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat therapy is often used to increase blood flow and relax tight muscles. Applying heat through hot packs or warm baths can soothe discomfort and improve the healing process.
Cold therapy, on the other hand, is beneficial immediately after an injury to help reduce inflammation and numb the affected area. Ice packs or cold compresses can significantly ease pain and swelling.
Combining both therapies can be effective; using heat to loosen tight muscles followed by cold to reduce inflammation can provide comprehensive relief from muscle strain.
It's crucial to apply these therapies correctly, ensuring that they do not exceed recommended durations to prevent skin damage or adverse effects.
Incorporating Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can be an essential component of recovery from muscle strain. A licensed physical therapist can evaluate the injury and develop a personalized rehabilitation program that includes specific exercises and modalities to promote healing.
Rehabilitation often includes a range of activities designed to restore strength, flexibility, and functionality to the affected muscle group. This structured approach helps prevent re-injury while ensuring a safe return to daily activities.
Education on body mechanics and posture is often included, empowering individuals to adopt safer movement patterns that reduce strain on their muscles in the future.
Additionally, ongoing assessments throughout the rehabilitation process help track progress and adjust the program as needed, ensuring optimal recovery.
Preventative Strategies for Long-Term Muscle Health
Preventing muscle strain involves an awareness of body mechanics and proactive measures. Warm-up routines before exercise and cooldowns afterward are crucial in preparing muscles for activity and promoting recovery.
Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet supports muscle health, as proper nutrition provides the necessary building blocks for muscle function and repair.
Incorporating cross-training into your fitness routine can also minimize the risk of overuse injuries, as it helps ensure varied muscle engagement and development.
Finally, listening to your body and taking appropriate rest days can prevent fatigue and overexertion, contributing to overall muscle health and well-being.