What Causes Muscle Strain and Tension?
Understanding Muscle Anatomy
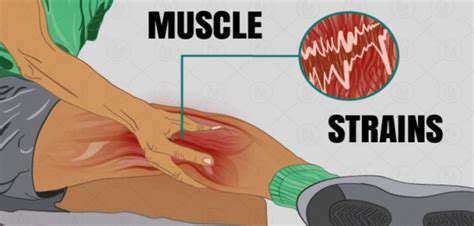
The human body consists of various muscle groups, each serving a specific function. Understanding the anatomy of these muscles is crucial for identifying the sources of strain and tension. When muscles are overstretched or overworked, they can experience strain, leading to discomfort and pain.
Muscles can be broadly classified into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are the ones most commonly involved in sports and physical activities, making them more susceptible to strain.
Common Activities That Cause Strain
Various everyday activities can lead to muscle strain, including improper lifting techniques, prolonged sitting, and intense workouts. Incorporating proper ergonomics and body mechanics can significantly reduce the risk of muscle injury. Simple actions like bending your knees while lifting can make a significant difference.
Sports and exercise, while beneficial for overall health, can also be a common source of strain if not approached with caution. Warm-up exercises and stretching are essential in preparing muscles for intense activity.
Symptoms of Muscle Strain and Tension
Recognizing the symptoms of muscle strain and tension is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion in the affected area.
In some cases, bruising may also occur, which indicates a more severe strain. Paying attention to these signs can help prevent further injury and promote quicker recovery.
Effective Treatment Strategies
When dealing with muscle strain, the R.I.C.E. method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is widely recommended. Resting the muscle allows it to heal, while ice applications can reduce swelling and pain.
Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort as the muscle heals. It is vital to avoid strenuous activities during the recovery period to ensure complete healing.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Future Strains
To avoid future muscle strains, implementing a regular stretching routine can greatly enhance flexibility and reduce tension. Consistency in warming up before physical activities is one of the best preventive strategies.
Strengthening exercises targeted at core stability can further protect against muscle strain. Building muscle resilience through balanced training ensures that muscle fibers are less likely to be injured during daily activities.
Recognizing Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Common Signs of Muscle Strain
Muscle strain often presents with a variety of symptoms that can help in identifying the condition. One of the most recognizable signs is localized pain in the affected area, which can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe pain. This pain may intensify with movement or when pressure is applied to the strained muscle.
Another common symptom is swelling or inflammation around the strained muscle. This can occur due to the body's natural inflammatory response, as blood flow increases in the area to promote healing. Swelling can sometimes lead to stiffness or reduced range of motion, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
Bruising may also be present, depending on the severity of the muscle strain. This occurs when small blood vessels rupture, leading to discoloration of the skin. The presence of bruising can indicate a more severe strain that may require medical attention.
Muscle spasms or cramping is another symptom associated with muscle strain. These involuntary contractions can be painful and can further limit mobility in the affected area. Muscle spasms often occur as a protective response from the body to prevent further injury.
Finally, weakness in the affected muscle is a key sign that a strain has occurred. Individuals may find it difficult to lift objects, perform physical activities, or even support their body weight on the strained muscle. This weakness is attributed to pain and potential damage to the muscle fibers.
Understanding Severity Levels of Muscle Strain
Muscle strains are typically classified into three severity levels: mild, moderate, and severe. Mild strains, or Grade I strains, involve a minor stretch or tear of the muscle fibers. Symptoms are usually mild, with minimal bruising and swelling, often allowing for a quick recovery.
Moderate strains, classified as Grade II, involve a more significant tear within the muscle fibers. Symptoms include more intense pain, noticeable swelling, and muscle weakness. Recovery may take longer, often requiring rest and rehabilitation exercises.
Severe strains, or Grade III, are complete tears of the muscle or tendon, which can result in significant pain, extensive swelling, and the inability to use the muscle at all. These strains often require medical intervention, including physical therapy or even surgical repair, depending on the extent of the injury.
Understanding the severity of a muscle strain is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment. It is important for individuals to assess their symptoms carefully and consult a healthcare professional if they suspect a severe strain that impairs their ability to function.
Timely intervention is essential in managing muscle strains effectively, as untreated severe strains can lead to complications such as chronic pain or long-term loss of function. Proper education on the symptoms and severity levels of muscle strains can help in making informed decisions about seeking treatment.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Muscle Strain
To minimize the risk of muscle strains, engaging in regular warm-up exercises is crucial. Warm-ups help prepare the muscles for physical activity by increasing blood flow and flexibility, reducing the likelihood of injury during more intense exercise. Simple techniques, such as dynamic stretches or light cardio, can be highly effective.
Strength training is another important preventive measure, as it builds muscle strength and endurance. Stronger muscles are less prone to strains. Incorporating core strengthening exercises can also improve stability and support to prevent injury during activities that involve sudden movements or heavy lifting.
Proper technique during physical activities is essential for preventing strains. Whether playing sports, lifting weights, or performing repetitive movements, using correct form can significantly reduce the risk of injury. Consulting a coach or trainer to learn proper techniques can be beneficial.
Listening to the body is vital in preventing muscle strain. Individuals should be aware of their limits and refrain from pushing through pain or fatigue. Recognizing the signs of overuse and taking necessary breaks will allow muscles to recover and adapt to physical demands.
Finally, maintaining hydration and a balanced diet contributes to overall muscle health. Muscles that are well-hydrated and nourished are better equipped to withstand physical stress. Incorporating foods rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals is essential for muscle recovery and strength.
Effective Treatments for Muscle Strain and Tension
Understanding Muscle Strain
Muscle strain is a common injury that occurs when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn. It can result from sudden movements, improper lifting techniques, or overexertion during physical activities. Understanding the nature of muscle strain is crucial for proper recovery and prevention of future injuries.
Symptoms of muscle strain can vary in intensity, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain. Common indicators include swelling, bruising, and limited mobility in the affected area. Recognizing these symptoms early on can lead to more effective treatment and a quicker return to normal activities.
To prevent muscle strain, it's essential to incorporate proper warm-up and cool-down routines into your exercise regimen. Additionally, focusing on strength training and flexibility exercises can help build resilience in your muscles and reduce the risk of injury.
At-Home Remedies for Muscle Tension
There are several effective at-home remedies for alleviating muscle tension, including the use of heat and cold therapy. Applying a warm compress can help relax and loosen stiff muscles, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. It's important to alternate between both methods depending on the stage of the injury.
Gentle stretching and yoga can also be beneficial for relieving muscle tension. Stretching helps increase blood flow to the muscles and improves flexibility, which can alleviate tightness. Simple yoga poses can promote relaxation and enhance overall muscle function.
Furthermore, staying hydrated plays a crucial role in muscle recovery. Drinking plenty of water ensures that your muscles remain well-hydrated, which helps reduce the risk of cramping and tension. Incorporating foods rich in electrolytes can also support muscle function and recovery.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many muscle strains can be managed at home, there are situations when it's essential to seek professional help. If the pain persists for more than a few days or worsens despite self-care, it may indicate a more serious injury that requires medical intervention.
Additionally, if you experience significant swelling, bruising, or an inability to move the affected muscle, consulting a healthcare professional is vital. They can provide accurate diagnosis and recommend a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for those with severe muscle strain or chronic tension. A trained therapist can develop a rehabilitation program that includes targeted exercises and modalities to enhance recovery and prevent future injuries.
Preventing Muscle Strain and Tension
Understanding the Causes of Muscle Strain
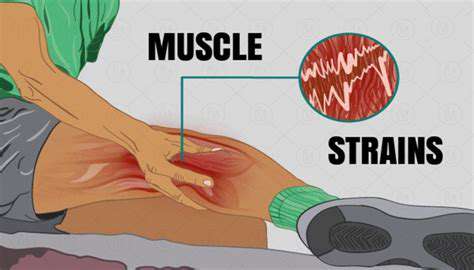
Muscle strain occurs when the fibers in a muscle are stretched or torn. Common causes include overexertion, improper lifting techniques, and inadequate warm-up exercises. Identifying these causes is essential in order to prevent further injury. Additionally, muscle imbalances and poor flexibility can contribute to the likelihood of strains.
Repetitive motions often cause muscle strain, especially in sports or jobs that require similar movements. Fatigue can also lead to strain as tired muscles are less able to cope with stress. Recognizing your body's limits is crucial for maintaining muscle health. Listening to your body and noting any areas of discomfort can help in these situations.
Your environment also plays a role in muscle strain. For example, working in awkward positions or on uneven surfaces increases the risk of injury. Proper ergonomics and workspace setup can significantly reduce this risk. Furthermore, ensuring that you are wearing appropriate footwear and maintaining good posture is vital for muscle safety.
Understanding personal risk factors is essential in preventing muscle strain. Being aware of age, fitness level, and previous injuries helps in tailoring a personalized prevention strategy. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide insights and recommendations. This proactive approach can help individuals avoid strain before it occurs.
Warm-Up and Stretching Techniques
Incorporating a proper warm-up routine can significantly reduce the risk of muscle strain. Activities like light jogging or dynamic stretches increase blood flow to the muscles. This prepares them for the physical demand that lies ahead. A well-structured warm-up also enhances overall performance.
Static stretching is an effective method to improve flexibility. Holding stretches for at least 20-30 seconds can increase the range of motion and reduce tightness. It's recommended to stretch muscles that will be engaged during activities. Being diligent about stretching can greatly help in preventing strains in the long run.
In addition to traditional warm-ups and stretches, incorporating foam rolling can be beneficial. Foam rollers help release muscle tightness and enhance tissue quality. This technique can be integrated as part of the warm-up or post-activity cool down. Regular use of foam rollers can lead to improved muscle performance.
Listening to your body during warm-up and stretching is crucial. If you feel any pain or discomfort, it's essential to adjust your routine. Not all muscles respond the same way, and individualized approaches may be necessary. Incorporating modifications based on personal needs ensures safety and effectiveness.
Strengthening and Conditioning Exercises
Strength training is a valuable tool in preventing muscle strain. Building muscle strength improves resilience against injury and enhances overall performance. Incorporating both resistance training and body-weight exercises can provide effective results. Variability in exercise routines also helps keep workouts engaging and comprehensive.
Focusing on core strength can be particularly beneficial. A strong core supports the entire body and helps maintain proper alignment during activities. Core exercises like planks, bridges, and rotations build stability and reduce strain on other muscle groups. This foundational strength can aid in injury prevention.
Balance and flexibility exercises also play a significant role. Incorporating activities like yoga or Pilates can enhance these aspects. Improved balance reduces the risk of falls and injuries during movements. Likewise, flexibility helps maintain a greater range of motion, further decreasing strain risk.
Consistency is key when it comes to strengthening and conditioning. Establishing a regular workout routine ensures that your muscles remain engaged and strong. Varying the intensity and type of exercises prevents plateauing. Monitoring progress and making adjustments is essential for ongoing improvement.
Post-Activity Recovery Strategies
After physical activities, recovery becomes crucial. Immediately following exercise, it's important to cool down properly with gentle stretches. This helps to gradually lower heart rate and prevent stiffness. Incorporating recovery practices in your routine aids muscle repair.
Hydration is often overlooked but is key for effective recovery. Proper fluid intake replenishes lost fluids and aids in muscle function. Drinking water or electrolyte-rich beverages can promote optimal recovery. Staying hydrated also helps reduce muscle cramps and fatigue.
Resting and allowing muscles time to recover is essential. Avoiding strenuous activities for a period after exercise helps prevent overuse. Listening to your body and taking rest days will facilitate better recovery. Quality sleep also enhances muscle repair, making it necessary to prioritize good sleeping habits.
Consider integrating treatments such as massage or physical therapy. Professional interventions can help alleviate soreness and promote healing. Regular massages can reduce tightness and enhance blood flow to the muscles. Consult with a professional to find the right recovery options tailored to your needs.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help is vital in managing muscle strain and tension. If pain persists despite self-care measures, consulting a healthcare professional is necessary. Continual discomfort could indicate a more serious underlying condition. Early intervention can lead to more successful recovery.
Other red flags include swelling, bruising, or difficulty moving the affected area. These symptoms may require immediate medical attention. A proper diagnosis ensures that appropriate treatments are provided. Ignoring severe symptoms could lead to further complications down the line.
Physical therapists play an essential role in recovery from muscle strain. They provide personalized assessments and create tailored rehabilitation plans. Working with a therapist can improve healing and help prevent future injuries. Regular follow-ups can ensure that progress is monitored effectively.
In some cases, additional imaging such as MRI or ultrasound may be necessary. These tools can help visualize the extent of the injury. Having a clear understanding of the condition can guide treatment options. Seeking help ensures that you stay informed and proactive about your muscle health.