Common Causes of Ear Infections
Understanding the Anatomy of the Ear
The human ear is a complex organ that plays a vital role in our ability to hear and maintain balance. It is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each part has specific functions and can be susceptible to infections under certain conditions.
The outer ear includes the parts we can see, known as the pinna, and the ear canal, which leads to the eardrum. Infections in this area are often called swimmer's ear and can be caused by moisture or bacteria entering the canal.
The middle ear is located behind the eardrum and houses the tiny bones that help transmit sound waves. Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the throat and are crucial for equalizing pressure. Blockages or dysfunction of these tubes can lead to fluid accumulation, creating an environment ripe for infections.
The inner ear contains structures that are essential for hearing and balance. While less commonly infected than the outer and middle ear, complications can arise from middle ear infections that spread to this region.
Understanding ear anatomy allows us to better recognize symptoms and triggers of infections, thereby aiding in prevention and management strategies.
Preventive Measures and Management Strategies
Preventing ear infections begins with maintaining proper ear hygiene. Regular cleaning of the outer ear with a damp cloth and avoiding cotton swabs can help prevent damage to the ear canal that may facilitate infections.
For children, ensuring that they are up to date on vaccinations, particularly the pneumococcal and flu vaccines, can significantly reduce the risk of developing ear infections, as these illnesses can lead to complications in the ear.
Managing allergies and avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke can also be crucial, as these factors can contribute to Eustachian tube dysfunction and increase the likelihood of infections.
If ear infections do occur, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. This may include antibiotics, pain relief, and in some cases, procedures to drain fluid from the middle ear.
Additionally, practicing good hand hygiene and keeping away from sick individuals can help prevent the spread of infections linked to ear problems. These strategies can help protect both children and adults from recurring ear infections.
Recognizing Symptoms of Ear Infections
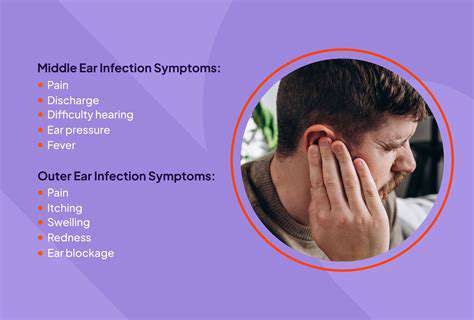
Common Symptoms to Watch For
When it comes to ear infections, recognizing the common symptoms is crucial for prompt treatment. Individuals may experience symptoms such as ear pain, which can vary in intensity. Children may also exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased irritability or difficulty sleeping. Other notable symptoms include fluid drainage from the ear and fever.
In some cases, patients experience hearing difficulties, which can be alarming. The sensation of fullness in the ear is another frequent complaint. Being aware of these symptoms can lead to quicker medical consultation, ultimately reducing the risk of complications.
It's important to differentiate between mild and severe symptoms as well. Mild symptoms might include slight discomfort or occasional itchiness, while severe cases could involve persistent pain or significant hearing loss. Timely recognition can be life-saving, particularly in children.
Keeping a close eye on changes, especially in young children who may not express themselves verbally, can help in identifying an ear infection early on. Family members should be familiar with these symptoms to ensure proper care.
Age-Related Symptoms of Ear Infections
Symptoms of ear infections can vary significantly based on a person’s age. Infants and toddlers often show different signs compared to adults. For instance, young children may tug at their ears or exhibit changes in feeding habits.
In older children and adults, symptoms may present more similarly to general illness, such as fatigue or malaise. Understanding these age-related distinctions is key for parents and caregivers to respond appropriately. Recognizing symptoms early can prevent escalation.
In the elderly, symptoms might be more subtle, often manifesting as confusion or a decrease in social engagement. Because of age-related vulnerabilities, it is advisable to be vigilant about changes in ear health among seniors. Regular check-ups can assist in early detection of potential infections.
Ultimately, awareness of age-specific symptoms can empower individuals and families to seek medical attention when necessary, aiding in better treatment outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Determining when to seek medical help for an ear infection can be challenging. If symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Immediate help should be sought if severe pain, high fever, or fluid drainage occurs. These symptoms could indicate a more serious infection.
It's also beneficial to follow up with a doctor if recurrent infections are experienced. Chronic ear infections can lead to permanent damage if left untreated. During follow-ups, medical providers can suggest preventive measures tailored to the individual's situation.
Parents should keep track of any ear infection history in their children to assist healthcare providers. This information may influence future treatment decisions. If a child’s behavior significantly changes, such as persistent crying or fussiness, a medical evaluation is warranted.
Ultimately, knowing when to seek help is crucial for preventing complications associated with ear infections and ensuring effective management of the condition.
Preventive Measures for Ear Infections
Preventing ear infections starts with maintaining good hygiene. Regular hand washing can reduce the risk of upper respiratory infections, which commonly lead to ear infections. It's especially vital for children who may be in close contact with others.
Breastfeeding infants can also decrease the likelihood of ear infections, as breast milk contains essential antibodies. Establishing a smoke-free environment is another preventative measure; secondhand smoke has been linked to increased risk of ear infections in children.
Vaccination plays a key role in prevention as well. Ensuring that children receive recommended vaccinations can help protect against diseases that may lead to ear infections. Staying informed about vaccines is an important responsibility for parents.
Finally, regular check-ups with healthcare providers can enable early detection and management of potential issues, allowing for proactive measures to be taken. Staying vigilant and informed is the best strategy for preventing ear infections.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections
Treatment Options for Ear Infections
When it comes to treating ear infections, the approach may vary depending on the severity and type of infection. For mild to moderate cases, healthcare professionals often recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. These medications can help alleviate discomfort while the body fights off the infection.
Antibiotics may be prescribed if the ear infection is bacterial in nature. It is crucial for patients to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This ensures that the infection is fully eradicated and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
In some chronic or severe cases, a surgical procedure may be necessary to insert ear tubes. These tubes help drain fluid from the middle ear and prevent future infections by providing ventilation. This option is often explored for children who experience recurrent ear infections.
Home remedies can also complement medical treatments. Warm compresses applied to the affected ear can provide soothing relief, and keeping the head elevated may assist in alleviating pressure. Herbal remedies, such as garlic oil, have been used by some as natural alternatives; however, one should consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatment.
Preventative Measures
Preventing ear infections begins with maintaining good hygiene. Regular handwashing can help reduce the spread of germs that may lead to respiratory infections, which are often precursors to ear infections. Teaching children the importance of cleanliness is particularly beneficial.
Vaccination plays a significant role in prevention as well. The pneumococcal vaccine and the flu vaccine can protect against certain infections that may contribute to ear infections. Consulting with a healthcare provider about the appropriate vaccinations for children is recommended.
Avoiding secondhand smoke is also vital, as exposure can affect the health of respiratory systems and increase the risk of ear infections. Families should aim to create a smoke-free environment, especially for young children.
Finally, ensuring that children are not exposed to allergens and irritants, such as pet dander or mold, can help prevent the buildup of congestion that may lead to ear infections. Regular cleaning and minimizing exposure to known allergens can support overall ear health.
Recognizing Symptoms Early
Being vigilant about the symptoms of ear infections can lead to early intervention, which is crucial for a successful outcome. Common signs include ear pain, which may be more pronounced while lying down. Children may also tug or pull at their ears, indicating discomfort.
Fever can accompany ear infections, particularly in young children, serving as another indicator of possible infection. Monitoring temperatures and looking for accompanying symptoms like irritability or difficulty sleeping should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Fluid drainage from the ear, whether clear or pus-like, can signal an ear infection that requires attention. Parents should note any changes in their child's behavior, such as increased fussiness or changes in appetite, as these can also signal discomfort.
Listening for unusual sounds, such as popping or bubbling noises inside the ear, can also provide clues, particularly in children. If these symptoms persist, seeking medical advice is essential to ensure appropriate treatment is received.
Long-Term Management and Care
For individuals who experience chronic ear infections, ongoing management strategies can help minimize outbreaks. Regular check-ups with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can monitor ear health and identify any persistent issues that may need addressing.
Managing allergies and avoiding allergens through tests and prescribed allergen avoidance strategies can also be key. Nasal sprays and medications may be recommended to help control allergic reactions that could lead to ear infections.
Hydration plays an important role in ear health. Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin mucus, thereby reducing ear congestion. Encouraging a healthy diet rich in vitamins C and E, along with probiotics, can strengthen the immune system.
Finally, ensuring that children grow out of pacifier dependencies or thumb-sucking behaviors after age two can aid in long-term ear health. Consulting with dental and medical professionals can provide guidance on breaking these habits if they persist.
Common Myths About Ear Infections
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding ear infections that can lead to ineffective treatments or undue anxiety. One common myth is that ear infections are always caused by bacteria, when in fact, many are viral and do not require antibiotics.
Another misconception is that all ear infections produce discharge. In reality, not all ear infections result in visible fluid leakage, and some children may experience persistent pain without any signs of drainage.
Some parents believe that excessive earwax causes ear infections; however, earwax serves a protective function by trapping dirt and bacteria. Maintaining good ear hygiene is important, but excessive cleaning can also lead to irritation and potential infections.
Lastly, many believe that ear infections only affect children. While they are indeed more common in children due to their anatomy, adults can experience ear infections as well, particularly those with allergies or respiratory issues. Understanding these myths can help parents manage expectations and seek appropriate care.
Preventing Ear Infections

Importance of Proper Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent ear infections. Regular handwashing can help to reduce the spread of germs that may lead to infections.
It's also crucial to keep the ears dry and clean. Moisture in the ears can create a breeding ground for bacteria.
Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, as this can push wax deeper and create blockages that may lead to infections.
Finally, ensure that any swimming or water activities are safe for the ears. Wearing earplugs or a swim cap can help to keep water out of the ears.
Vaccination and Health Check-ups
Vaccinations play a vital role in preventing ear infections, especially in children. Ensuring that children are up-to-date on their vaccinations can lower their risk of respiratory infections, which can lead to ear infections.
Regular health check-ups are also important. These check-ups can help in identifying and treating any underlying conditions that may predispose an individual to ear infections.
If a child is prone to ear infections, consulting with a pediatrician can provide tailored strategies for prevention and intervention.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for reducing the risk of recurrent ear infections.
Managing Allergies and Environmental Factors
Allergies can significantly influence the health of the ears. If you or your child have allergies, managing them effectively may reduce the frequency of ear infections.
Using air purifiers and keeping the home free of dust and allergens can contribute to ear health.
Furthermore, avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke and other pollutants is critical, as these can irritate the respiratory system and lead to infections.
Identifying triggers and working with an allergist can provide valuable insights into managing allergies and preventing related ear infections.
Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Early Treatment
Being aware of the symptoms of ear infections is essential for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include ear pain, irritability in children, and difficulty sleeping.
If you suspect an ear infection, it's vital to seek medical attention. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
Additionally, knowing when to seek care is crucial. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare provider is advisable.
Managing pain and discomfort through appropriate over-the-counter medications can help while waiting for a medical appointment.