Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure imbalances are a critical concern in neurological health. Maintaining the appropriate CSF pressure is essential for proper brain function, and deviations from the normal range can lead to a variety of serious neurological complications. Understanding the causes, mechanisms, and consequences of these imbalances is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
These imbalances can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from benign conditions to life-threatening diseases. Early detection and intervention are vital in mitigating potential damage and improving patient outcomes.
Causes of CSF Pressure Imbalances
Several factors can contribute to CSF pressure imbalances. These include traumatic brain injuries, infections, tumors, and inflammatory conditions. Head trauma, for example, can disrupt the delicate balance of CSF pressure, leading to either a rise or a fall in the pressure within the intracranial space.
Additionally, certain medical conditions and treatments can affect CSF production, absorption, or flow, further contributing to imbalances.
Symptoms of CSF Pressure Imbalances
Recognizing the symptoms of CSF pressure imbalances is crucial for prompt medical attention. Symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the imbalance. Headache, nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances are common indicators. These symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked, hence the importance of regular neurological check-ups.
In severe cases, symptoms can include seizures, loss of consciousness, and even coma.
Diagnosis of CSF Pressure Imbalances
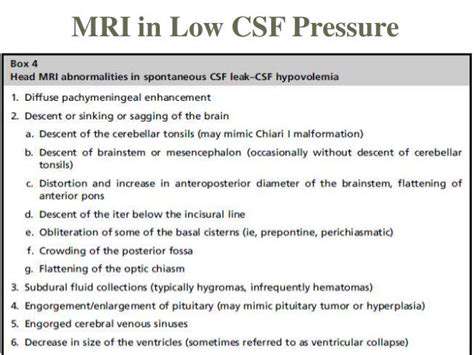
Diagnosing CSF pressure imbalances requires a comprehensive approach. Medical history and a thorough neurological examination are essential initial steps. Diagnostic tools, such as lumbar punctures (spinal taps) and imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs, help pinpoint the cause and extent of the imbalance.
Treatment Options for CSF Pressure Imbalances
Treatment strategies for CSF pressure imbalances vary depending on the underlying cause. Medical interventions may involve medications to manage underlying conditions, surgical procedures to address structural issues, or drainage techniques to reduce excessive pressure. The chosen approach is tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
Close monitoring and supportive care are often necessary to manage the symptoms and prevent further complications.
Long-Term Management and Prognosis
Long-term management of CSF pressure imbalances is crucial for minimizing the impact on the patient's quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments, adherence to medical recommendations, and lifestyle adjustments play a critical role in preventing exacerbations and potential complications. The prognosis for patients with CSF pressure imbalances depends significantly on the promptness and effectiveness of treatment and the underlying cause.
Early intervention and consistent management often lead to positive outcomes and improved quality of life.