A Novel Approach to Migraine ManagementCGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) inhibitors represent a newer class of migraine treatments. These medications directly target CGRP, a neuropeptide that plays a significant role in migraine pathophysiology. CGRP inhibitors can be administered via injection or oral medication, offering various options for patients to manage their migraines. The potential for long-term preventive efficacy and a favorable safety profile make CGRP inhibitors a compelling option, particularly for individuals who have not found relief with other treatments. However, it's important to be aware of potential side effects, which may vary depending on the specific medication and individual.
Switching Between Botox and CGRP Treatments: Considerations
Patients who experience migraines may find that switching between Botox and CGRP inhibitors can provide a more comprehensive approach to managing their condition. The temporary nature of Botox's preventive effect may necessitate exploring CGRP inhibitors for long-term management. Conversely, if CGRP inhibitors are not sufficiently effective, Botox injections might be considered as an additional or alternative treatment. Individual responses to both treatments can vary, and careful consideration of a patient's specific needs, triggers, and symptoms is essential for making informed decisions regarding treatment strategies, potentially including a combination therapy approach.
Botox: A Neuromodulatory Approach
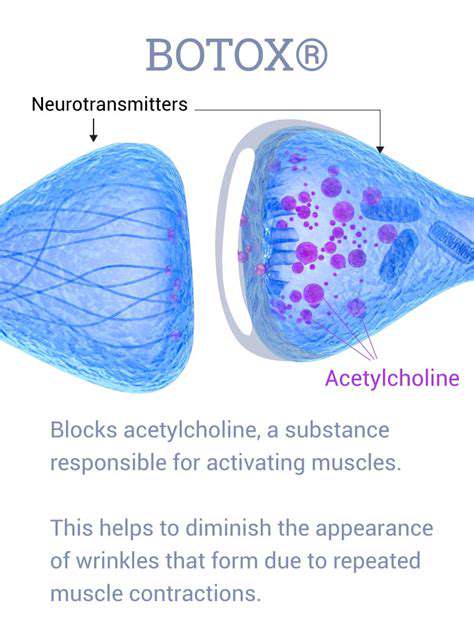
Understanding the Neuromodulatory Mechanism
Botox, a neurotoxin derived from the bacterium *Clostridium botulinum*, works by temporarily blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter crucial for muscle contraction. This disruption of the neuromuscular junction leads to a temporary paralysis of the targeted muscles. The precise mechanism involves the toxin binding to SNARE proteins, essential for vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release. This intricate process results in a significant reduction in muscle activity, which is the basis for Botox's therapeutic applications.
Understanding this mechanism is vital for appreciating the diverse range of applications and potential side effects. The temporary paralysis achieved allows for the relaxation of muscles involved in wrinkles and other aesthetic concerns, while also having applications in treating various medical conditions involving excessive muscle contractions.
Therapeutic Applications and Considerations
Botox's neuromodulatory properties extend far beyond cosmetic enhancements. It finds significant use in treating a variety of medical conditions, including excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), migraines, and strabismus (crossed eyes). In these cases, Botox's ability to inhibit muscle activity provides relief from symptoms by reducing excessive or abnormal muscle contractions.
Beyond these applications, it's crucial to acknowledge potential side effects. While generally safe, Botox injections can sometimes cause temporary bruising, pain, or muscle weakness at the injection site. Rarely, more serious side effects, such as difficulty swallowing or breathing, may occur, making careful consideration of the risks and benefits essential before undergoing treatment.
Careful selection of the appropriate treatment area, dosage, and frequency is crucial for maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks. The complexity of the individual patient's needs and medical history must be meticulously evaluated to ensure optimal results and mitigate any complications. Consulting with a qualified medical professional is essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of Botox treatment for each specific case.
The precise targeting of muscle activity is a key aspect of Botox's effectiveness. Careful consideration of the specific muscles and their function in the context of the condition being treated is critical for achieving successful outcomes.
Furthermore, long-term effects and potential cumulative impacts of repeated Botox treatments require ongoing observation and research. The multifaceted nature of the treatment warrants a comprehensive understanding of the short-term and long-term impacts on the neuromuscular system to ensure patient safety and well-being.

Disclaimer: All articles on this site are original, please do not reprint


